FIGURE 5.
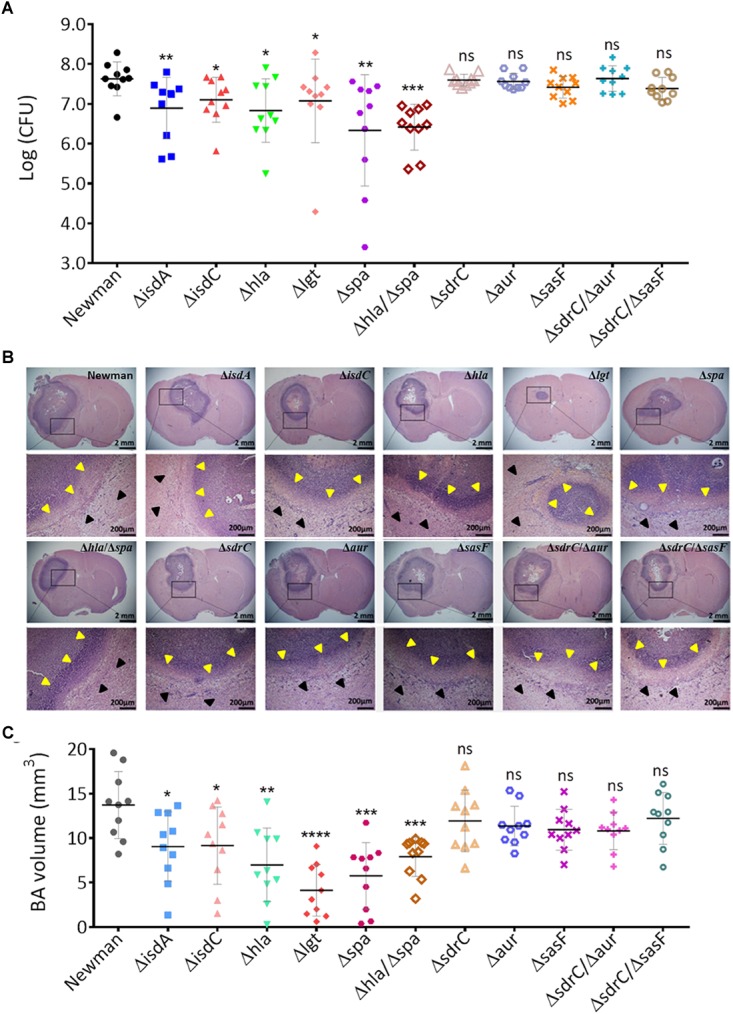
Isogenic mutant analysis of virulence determinants that contribute to BA formation through S. aureus infection. (A) CFU enumeration of wild-type Newman and mutant strains in the BA model. Groups of 10 mice each were challenged intracranially with 5 μl of agarose beads encapsulated with 1 × 105 CFU of S. aureus. At 5 days after infection, the number of the viable organisms associated with BA was determined by quantitative culture. Titers are expressed as the mean log (CFU) per mouse in the brain homogenate. (B) H&E-stained brain sections collected from mice at 5 days post infection with wild-type Newman or mutant strains. For each strain, sections collected from a representative mouse brain revealed a focal intracerebral lesion (20×, top panel) and a well-defined abscess surrounded by a clear boundary (yellow arrows) within the normal brain tissue (black arrows, 400×, bottom panel). (C) BA volume calculation of mice infected with the wild-type Newman or mutant strains. The abscess areas of each brain section slide were evaluated.
