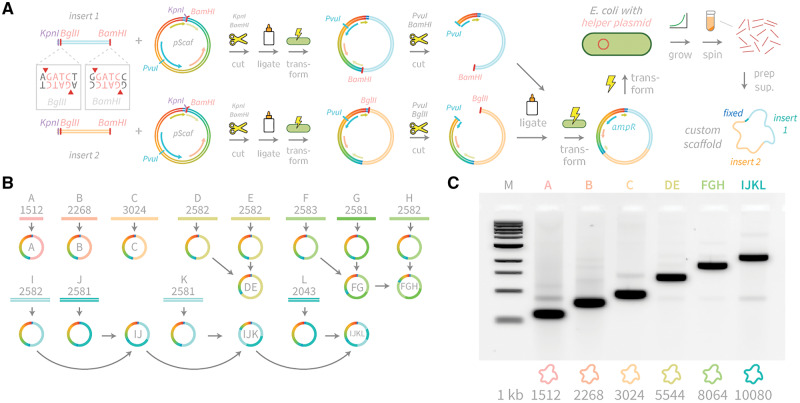
Figure 3.
Cloning scheme and gel analysis of new scaffolds. (A) Custom sequence inserts are PCR-amplified with a forward primer containing KpnI and BglII sites and reverse primer containing a BamHI site. Inserts up to 3 kb in length were directly transformed into E. coli bearing helper plasmid. Larger scaffolds can be assembled by iterative PvuI+BamHI digestion of the vector containing the 5′ fragment, and PvuI+BglII digestion of the vector containing the 3′ fragment, followed by ligation, transformation and miniprep. (B) Twelve inserts (A–L) were cloned into pScaf vector at the KpnI-BamHI site. Inserts A, B and C were used to produce scaffolds with lengths of 1512, 2268 and 3024 bases. Larger scaffolds were assembled in multiple rounds as shown. (C) All scaffolds were grown in XL1-Blue cells containing helper plasmid M13cp, recovered and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis to determine purities ranging from 46% to 83%.