Figure 1.
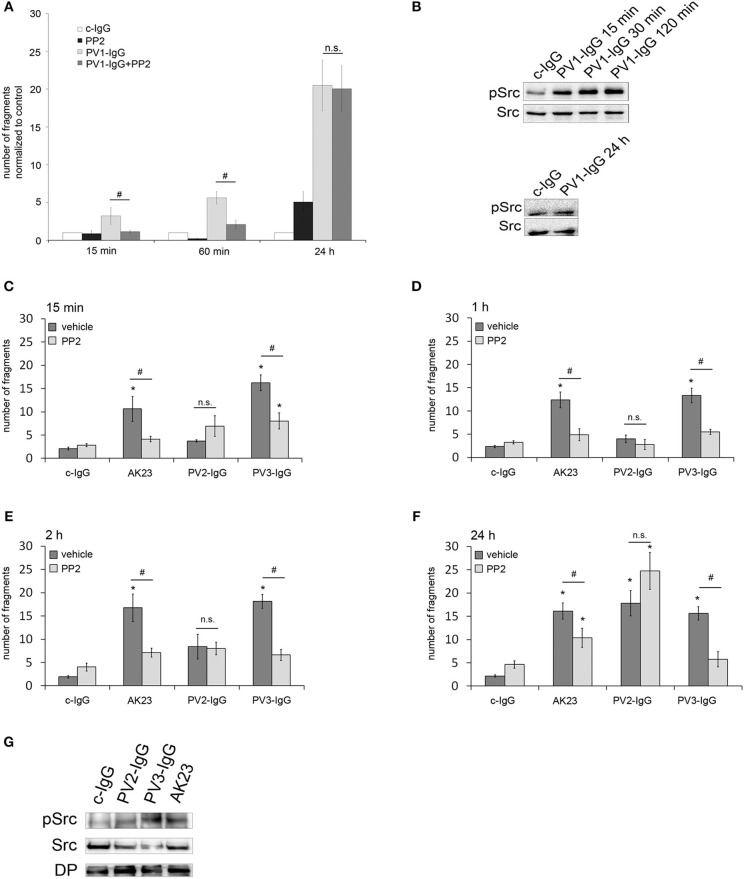
Protective effect of Src inhibition against autoantibody-induced loss of cell cohesion is variable. (A) HaCaT cells were incubated with PV1-IgG or with control IgG (c-IgG) and subjected to dispase-based dissociation assays. Inhibition of Src by PP2 prevented fragmentation of cell monolayers after incubation with PV1 for 15 min and 60 min but not for 24 h (n = 5; #p < 0.05; *p < 0.05 vs. c-IgG). (B) Western blot analysis revealed that Src was phosphorylated after 15, 30, and 120 min but not after 24 h of incubation with PV1 (n = 3). (C–F) PV2- and PV3-IgG as well as AK23 were applied for several time points: 15 min (C), 1 h (D), 2 h (E), and 24 h (F), with keratinocytes being subsequently subjected to dissociation assays. Co-incubation with PP2 led to significantly reduced fragment numbers in PV3-IgG- and AK23- but not PV2-IgG-treated cells (n > 7; #p < 0.05; *p < 0.05 vs. c-IgG). (G) Corresponding Western blot analysis for 2 h revealed that all autoantibody fractions were effective to activate Src (n = 3).