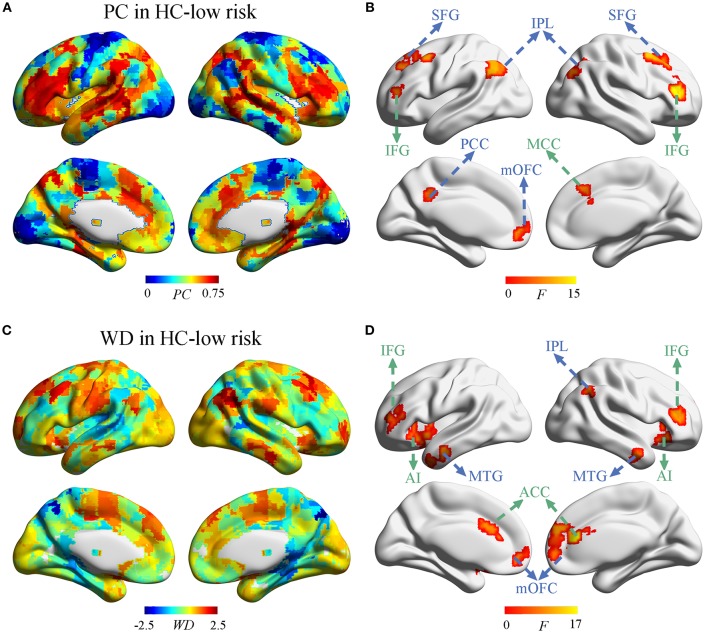
Figure 3.
The distribution of PC and WD in the whole brain. (A) The PC distribution in HC-low risk. (B) Significant effects of vascular burden on PC were observed in the DMN (such as bilateral superior frontal gyrus [SFG], inferior parietal lobule [IPL], and left posterior cingulate cortex [PCC], medial orbitofrontal cortex [mOFC]) and the ECN (such as bilateral inferior frontal gyrus [IFG] and right midcingulate cortex [MCC]) (P < 0.01, FDR corrected). (C) The WD distribution in HC-low risk. (D) The WD was significantly regulated in the regions of DMN (such as bilateral mOFC, middle temporal gyrus [MTG], and the right IPL) and the ECN (such as bilateral ACC, IFG, and anterior insula [AI]) (P < 0.01, FDR corrected). HC, healthy control; PC, participant coefficient; WD, within module degree.