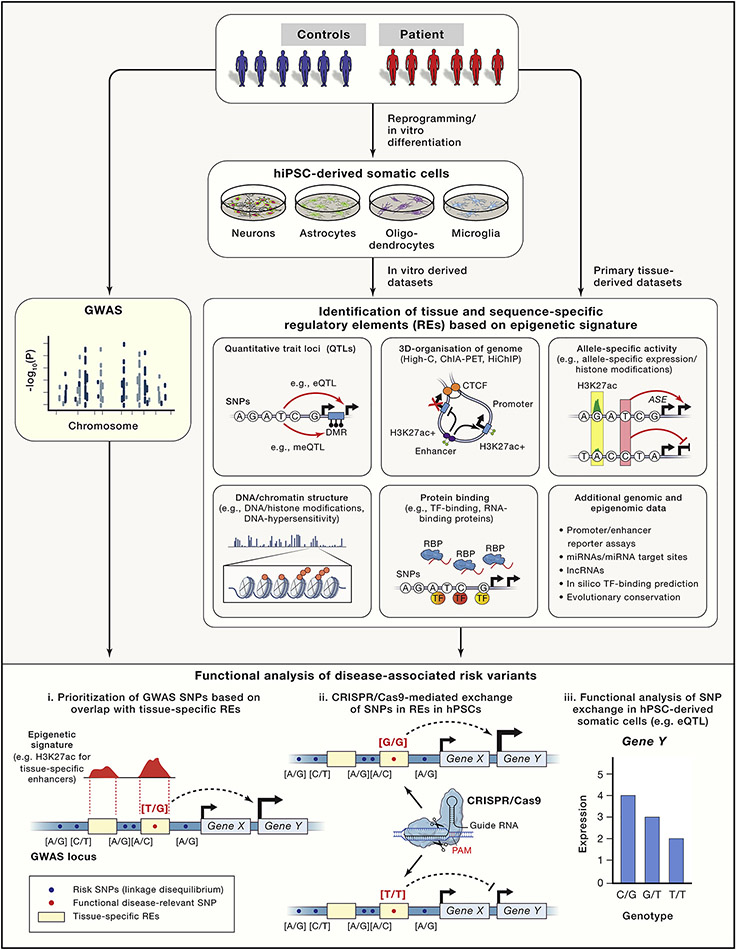
Figure 2: Identification of functional risk variants based on epigenetic signatures.
Candidate disease-associated risk variants (e.g.SNP) are prioritized based on integrating GWAS data with a variety of epigenetic datasets. Risk variants overlapping with tissue-specific regulatory elements are more likely to be functional compared to risk variants outside of regulatory elements. Epigenetic datasets can be generated either from primary tissue or from in vitro hPSC-derived somatic cell types. Schema at the bottom depicts (i) the identification of a hypothetical GWAS identified diseases-associated risk variant overlapping with a brain-specific distal enhancer (indicated by enrichment for histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation Chip-seq signal), (ii) the CRISPR/Cas9 mediated SNP exchange and (iii) the functional analysis of the SNP exchange indicated by a genotype-dependent cis-regulatory effect on expression of Gene Y (eQTL).