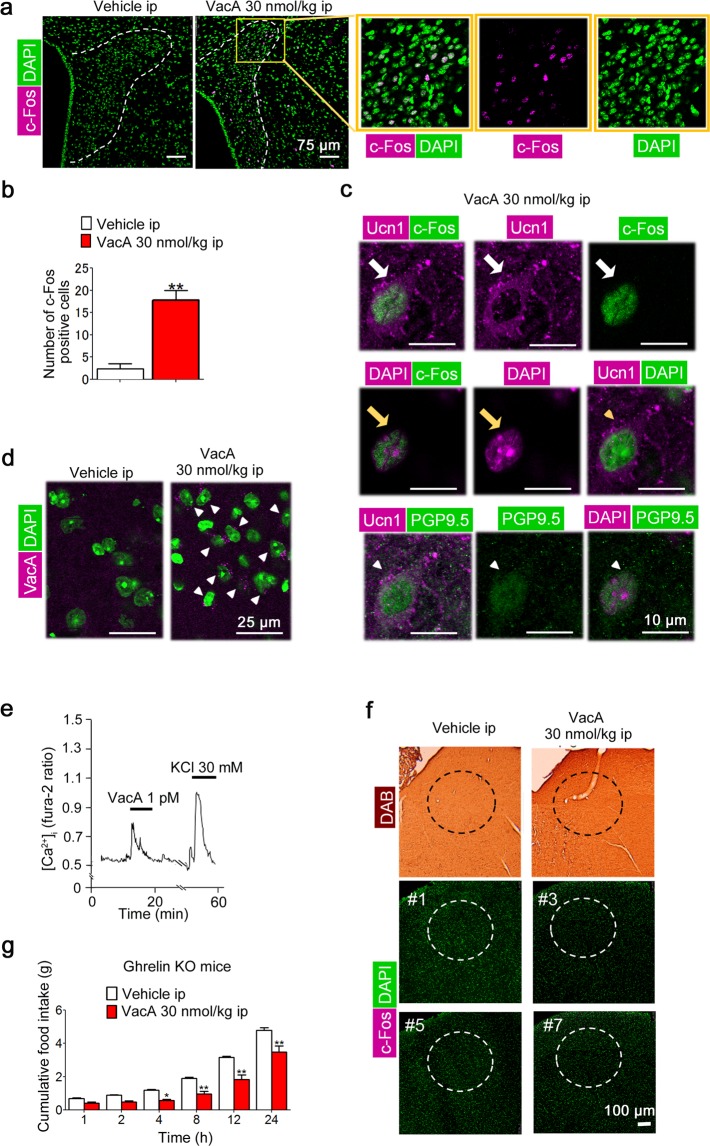
Figure 3.
Peripheral VacA administration directly induces neuron activity in hypothalamus. Each brain was isolated and fixed with 4% PFA and 0.5% GA in 0.1 M PB 4 h after IP administration of 30 nmol/kg bw of VacA. Coronal sections of the PVN were stained with an anti-mouse c-Fos and/or Ucn1antibody. (a) Representative images of the c-Fos-positive cells in the PVN using immunofluorescent staining. (b) The number of c-Fos-positive cells in the PVN was counted on one side of the PVN (n = 4). (c) Representative images of c-Fos- and Ucn1-positive (white arrows), c-Fos- and DAPI-positive (yellow arrows), Ucn1- and DAPI-positive cells (yellow arrow heads), or Ucn1- and PGP9.5-positive cells (white arrow heads) in the PVN cells. (d) Representative images in the hypothalamus obtained after immunofluorescent staining with VacA antibody (arrows). (e) Representative [Ca2+]i oscillations (Fura-2 ratio) in single cells administered 1 pM of VacA. (f) Representative images of c-Fos-positive cells in the NTS obtained after DAB or immunofluorescent staining (# number indicates an individual animal) are shown. (g) Cumulative food intake was measured for 24 h in ghrelin-KO mice receiving IP VacA administration. TBS was administered as the control. The values are presented as the means ± SEM. Differences were considered significant at *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.