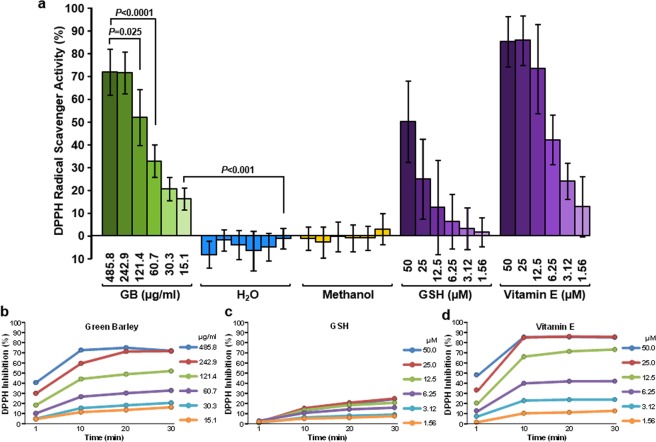
Figure 2.
GB exhibits potent anti-oxidant activity evidenced by DPPH free radical scavenging assay in a dose and time-dependent manner. (a) A gradient of GB concentrations (485.8 µg/ml to 15.1 µg/ml) were incubated with DPPH for 30 min at room temperature, and the absorbance at 517 nm was recorded. DPPH radical scavenging activity was calculated according to the equation described in materials and methods. Glutathione (GSH) and vitamin E (50 to 1.56 µM) were included as positive antioxidant controls and analyzed concomitantly. Water was used as a solvent control, whereas methanol was used as a blank. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of five independent experiments. Two-tailed paired Student’s t-tests were accomplished to determine the statistical significance of two experimental samples (P values). GB serial dilution concentrations (1:2; 485.8 to 15.1 µg/ml) were incubated with DPPH for 1, 10, 20 and 30 min at room temperature and the absorbance at 517 nm was recorded. Glutathione (GSH) (c) and vitamin E (50 to 1.56 µM) (d) were included as positive antioxidant controls and concurrently analyzed. Data are shown as the average of five independent experiments.