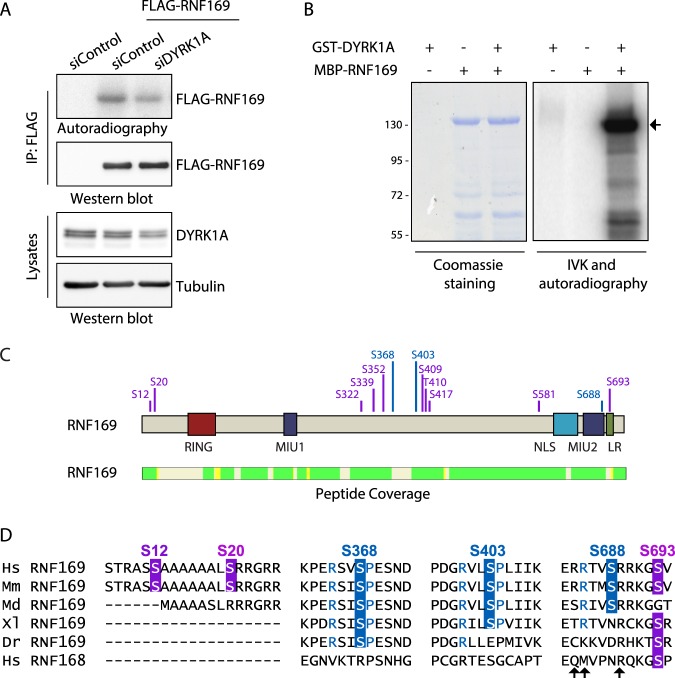
Figure 5.
RNF169 is a DYRK1A substrate. (A) FLAG-tagged RNF169 expressed in HEK-293T cells depleted of DYRK1A by siRNA transfection was purified using an anti-FLAG Ab and subsequently used in an IVK assay in the presence of radioactive labeled ATP. Proteins were analyzed by autoradiography and in WBs probed with an anti-FLAG Ab to check for equal amounts of RNF169 protein. DYRK1A depletion was assessed in WBs of total lysates from parallel samples. Quantification is shown in Fig. S5E. (B) A radioactive IVK assay was performed using bacterially produced MBP-RNF169 in the absence or presence of GST-DYRK1A. The background DYRK1A autophosphorylation was determined by incubation of the protein alone. The Coomassie blue staining demonstrates equal loading and the arrow points to MBP-RNF169. (C) MBP-fused RNF169 was used as a substrate in IVK assays with GST-DYRK1A and the phosphorylated peptides were identified by MS analysis. The position of the phosphorylated aa is in violet and the validated residues are in blue. The peptide coverage of RNF169 is also shown (identified peptides in green), rendering a coverage of 87%. See Fig. S6E,F for validation experiments. (D) Evolutionary conservation of the DYRK1A-dependent phosphosites in RNF169. Alignment of the RNF169 proteins from different the species and human RFN168: Dr, Danio rerio; Hs, Homo sapiens; Md, Monodelphis domestica; Mm, Mus musculus; Xl, Xenopus laevis. The phosphosites validated in the IVK assays are shown in blue, with residues at P − 3 and P + 1 in the same color if matching the DYRK1A consensus phosphorylation site. The putative phosphosites assayed in IVK assays but not validated are shown in violet. The arrows indicate residues important for the interaction with the ubiquitinated nucleosome41.