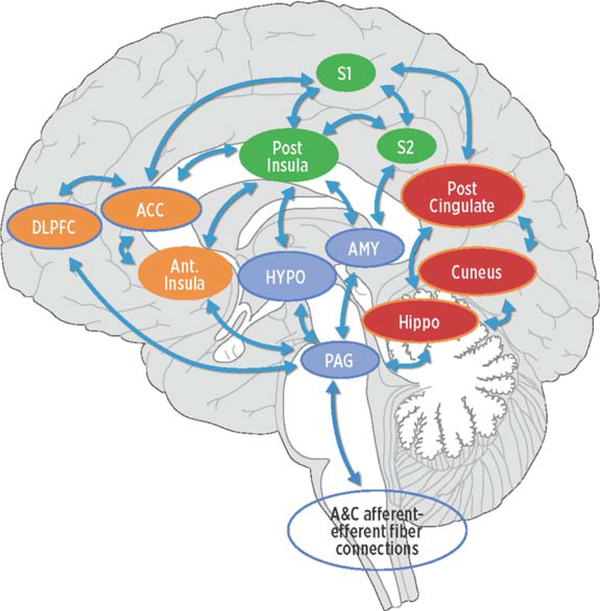
Fig. 1.
Conceptual model of four networks believed to be involved in pain processing and pain interpretation. Green areas represent common structures in the sensory/discriminative (lateral) pain pathway (pINS, S1, and S2). Orange areas represent common structures identified in the affective/motivational (medial) pain pathway (ACC, AINS, dlPFC). The blue regions represent common structures in the descending modulatory system (AMY, HYPO, PAG). Red areas represent core structures in the default mode network (posterior cingulate gyrus, cuneus, hippocampus). The arrows represent multiple cortical connections between regions and systems indicating the complex interconnectedness of brain regions involved with pain. pINS, posterior insula; S1, primary somatosensory cortex; S2, secondary somatosensory cortex; ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; aINS, anterior insula; dlPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; AMY, amygdala; HYPO, hypothalamus; PAG, periaqueductal gray.