Fig. 3.
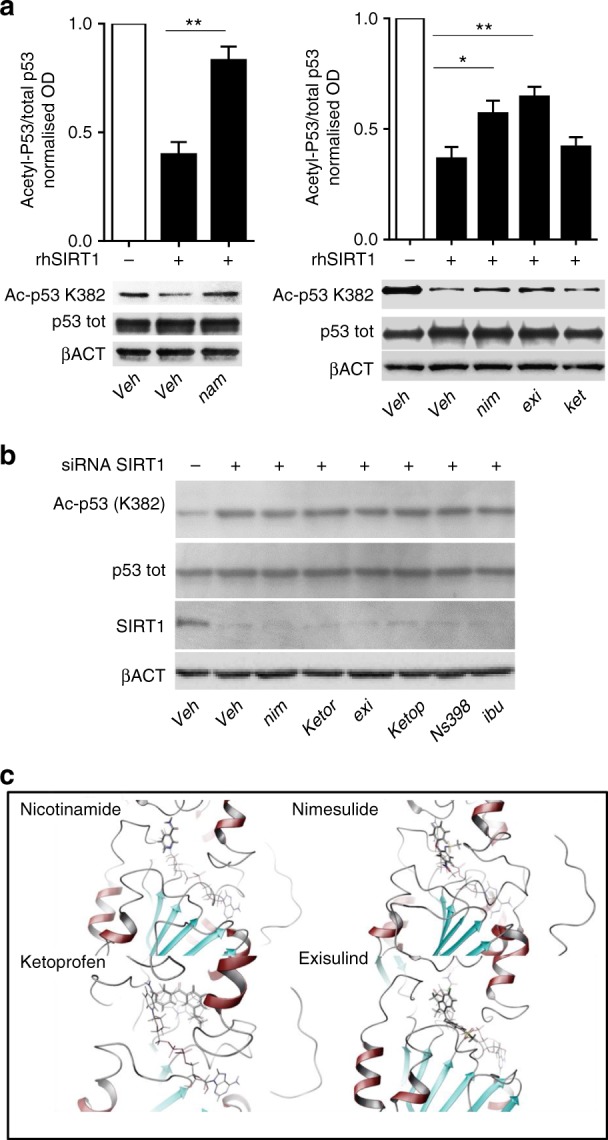
The NSAIDs-induced acetylation at the K382 residue is mediated by SIRT1 inhibition. a Deacetylation assay on native p53 protein. Picture shows a representative immunoblot analysis of native acetylated and total p53 present in the extracts of MDA-MB-231 6 h before harvesting, cells were treated with 20 etoposide μM to obtain sufficient amount of p53 acetylation; the same batch of protein extract was divided in 15 µg aliquots and treated either with vehicle (veh) or with 300 µM nicotinamide (nam), nimesulide (nim), exisulind (exi), ketoprofen (ket) as described in Materials and Methods paragraph, the extract was then treated with rhSIRT1 or with saline buffer. β-actin is reported as loading control. Quantification of the immunoblot signals are reported in the inserted graph: acetylated p53 signal was normalised on the corresponding total p53 signal and referred to the veh/- SIRT1 sample. Bars represent the average ± SEM normalise values of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 **P < 0.01 P-values were calculated by Student’s t-test. b Immunoblot analysis of p53 acetylation at K382 site in SIRT1 knock-down MDA-MB-231 cells. MDA-MB-231 expressing siRNA SIRT1 were treated with 270 μM vehicle, nimesulide, ketorolac, exisulind, ketoprofen, NS398, ibuprofen. β-actin is reported as loading control. c Best docking poses for selected SIRT-1 inhibitors. Data from more NSAIDs are shown in Fig. S3A. The enzyme is shown as ribbon, inhibitors are shown in stick representation. Nicotinamide, nimesulide, and exisulind overlap NAD binding site; ketoprofen overlaps the EX527-analog binding site only after its relevant structural deformation
