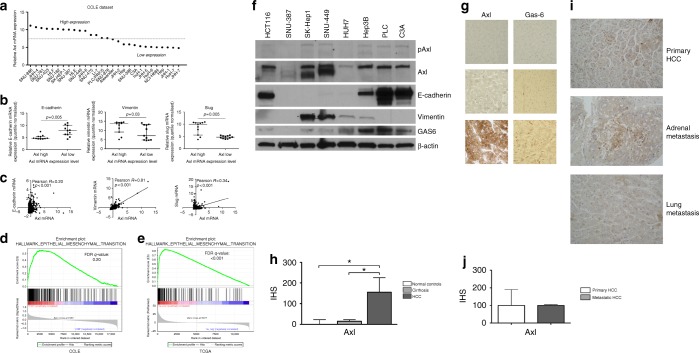
Fig. 1.
Axl overexpression is a common feature of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and is associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). a Differential expression of Axl mRNA in a panel of 28 immortalised HCC cell line from the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) dataset confirming Axl over-expression in 13/28 cell lines. b, c The relationship between the expression of Axl and EMT-related genes including E-Cadherin, Vimentin and Slug in the CCLE (b) and in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) HCC RNA-seq dataset (n = 373). d, e GSEA on the CCLE RNA-seq dataset of 28 HCC cell lines (d) and TCGA dataset (e) confirmed enrichment of EMT-related transcripts in Axl-overexpressing cell lines (FDR q = 0.20 and q < 0.001, respectively). f Analysis of the expression of Axl and related total and phosphorylated protein by Western blotting in a panel of 7 HCC cell lines with colorectal cancer HCT116 cell lines serving as positive controls. g Representative sections of normal (n = 10), cirrhotic (n = 10) livers and HCC (n = 10) demonstrating Axl and Gas-6 expression by immunohistochemistry. HCC samples display a strong, membranous staining for Axl in neoplastic cells and scattered Gas-6 expression in peri-tumoural Kupffer cells. h The distribution of Axl expression by immunohistoscores (IHS) across normal, cirrhotic liver tissues and HCC (n = 10 in each group) demonstrating significant Axl overexpression in tumour samples. i Representative sections demonstrating Axl expression in matched primary and metastatic HCC specimens. j The distribution of Axl expression in primary and metastatic HCC samples (n = 12) derived from 5 patients