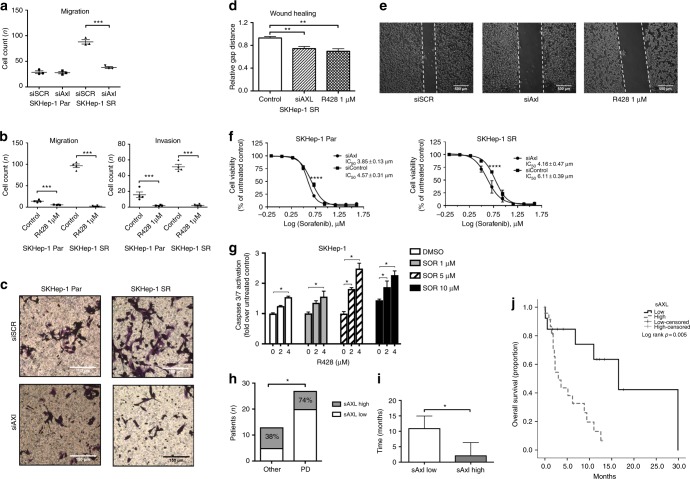
Fig. 4.
Axl modulates the motility and invasive capacity of immortalised hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and determines sensitivity to sorafenib in immortalised cell lines and in patients with HCC. a, b Inhibitory effect of shRNA-mediated Axl silencing on SKHep-1 and SKHep-1SR cell motility and invasion capacity. c Inhibitory effect of R428 on SKHep-1 and SKHep-1SR cell motility and invasion. d, e Wound healing assays confirming shRNA and R428-mediated repression of cell motility secondary to Axl inhibition. f Inhibition of Axl by shRNA augments the sensitivity of SKHep-1 and SKHep-1SR cells to sorafenib. g Incremental effect of R428 on sorafenib-induced apoptosis of SKHep-1 cells as measured by Caspase 3/7 activation ratios against controls. h The relationship between pre-sorafenib serum sAxl levels and cause of treatment discontinuation in patients receiving sorafenib for HCC (n = 40). i Patients with elevated sAxl levels had significantly shorter duration of sorafenib therapy with earlier discontinuation compared to patients with lower sAxl levels at baseline. j Kaplan–Meier curves showing the effect of high baseline sAxl levels in predicting for worse overall survival in patients with HCC undergoing sorafenib therapy