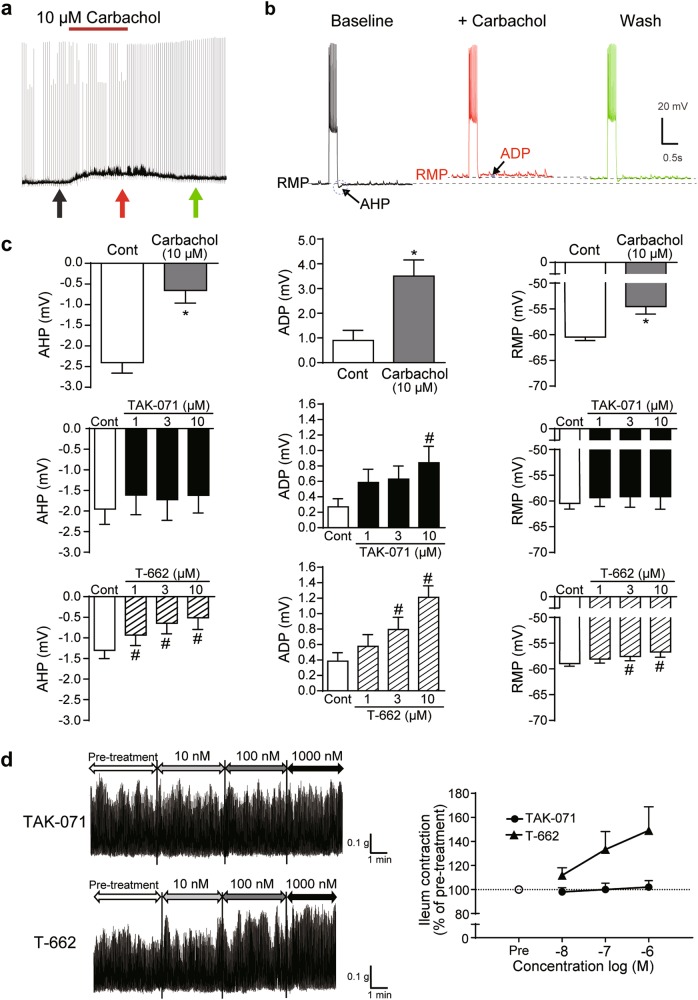
Fig. 2.
Unlike T-662, TAK-071 selectively induced afterdepolarization in layer 5 pyramidal neurons and did not increase spontaneous ileum motility in vitro. a Chart recording of the membrane potential of a layer 5 pyramidal neuron with bath-applied carbachol (10 µM for 10 min). Brief current steps (~450 pA) delivered at 20 s intervals generated short periods of activity. b Individual responses to current injections shown at the times indicated by arrows in a, with expanded views of the AHPs and ADPs superimposed. c Summary graph comparing mean changes in AHPs, ADPs, and RMPs following the bath application of carbachol, TAK-071, or T-662 for 10 min. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5); *p ≤ 0.05 compared with the vehicle (veh)-treated group by paired t-test; #p ≤ 0.05 compared with the veh-treated group by a paired Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. d Effects of TAK-071 and T-662 on spontaneous ileum motility in mice. Data are shown as representative traces (left) and the percent change of ileum contraction from the baseline measured at pre-treatment (right, n = 8). ADP afterdepolarization, AHP afterhyperpolarization, RMP resting membrane potential, SEM standard error of the mean