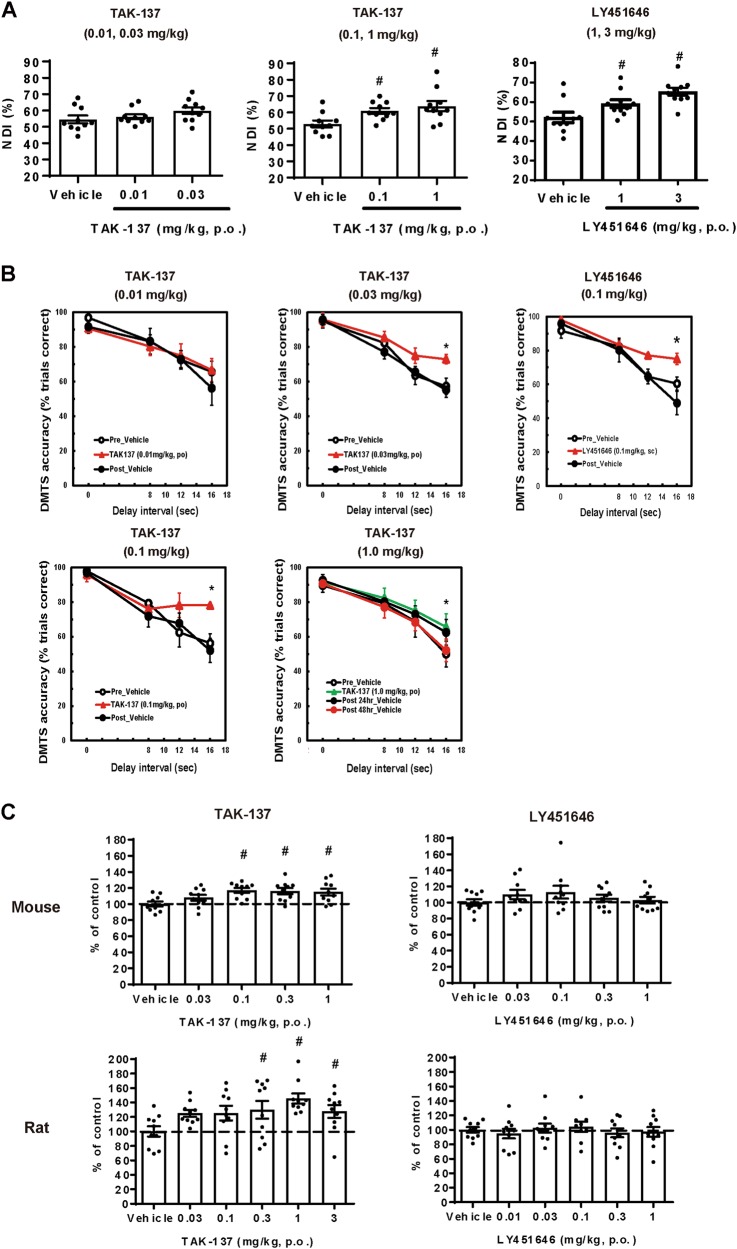
Fig. 4.
TAK-137 produced potent cognitive improvement in rats and monkeys and induced proliferation of rodent hippocampal neural progenitor cells over a broader range of doses compared to LY451646. a Cognitive-enhancing effects of TAK-137 and LY451646 on rat NORT. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 10). Significant difference from vehicle-treated group was analyzed using the one-tailed Williams’ test (TAK-137: #P ≤ 0.025, d.f. = 27, t = 2.3 (0.1 mg/kg), 3.2 (1 mg/kg), LY451646: #P ≤ 0.025, d.f. = 27, t = 2.2 (1 mg/kg), 4.2 (3 mg/kg)). b Cognitive-enhancing effects of TAK-137 and LY451646 on monkey DMTS task. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 4). Significant difference from vehicle-treated group was analyzed using two-way ANOVA (TAK-137: *P ≤ 0.05, F1, 6 = 4.0 (0.03 mg/kg), F1, 6 = 6.7 (0.1 mg/kg), F1, 6 = 6.1 (1 mg/kg), LY451646: *P ≤ 0.05, F1, 6 = 7.2 (0.1 mg/kg)). c Effects of TAK-137 and LY451646 on the number of BrdU-positive cells in mouse or rat hippocampus. TAK-137 or LY451646 was orally administered to mice or rats for 4 days and tissues were isolated the next day. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 9-10). Significant difference from vehicle-treated group was analyzed using the one-tailed Williams’ test (mouse: #P ≤ 0.025, d.f. = 45, t = 3.3 (0.1 mg/kg), 3.2 (0.3 mg/kg), 3.1 (1 mg/kg), rat: #P ≤ 0.025, d.f. = 54, t = 2.4 (0.3 mg/kg), 3.7 (1 mg/kg), 3.0 (3 mg/kg))