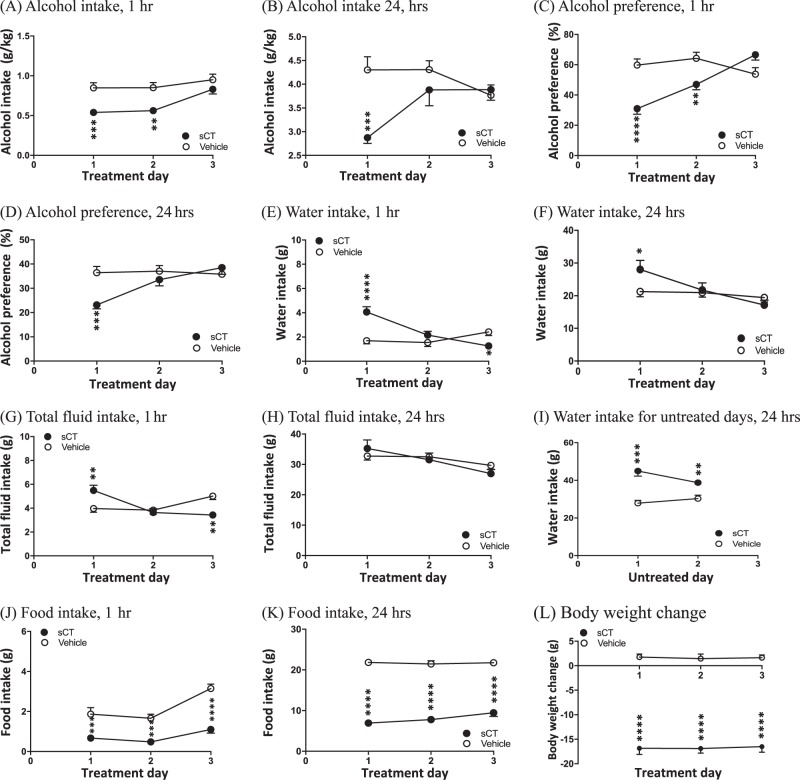
Fig. 1.
Repeated sCT administration attenuates voluntary alcohol intake, alcohol preference, and food intake and decreases body weight in outbred rats. a Repeated sCT treatment (5 μg/kg, IP) reduced alcohol intake in rats (N = 25) in the intermittent access 20% alcohol two-bottle-choice drinking paradigm at the time point of 1 h on the first and second treatment days compared to vehicle (N = 25). b Repeated sCT administration reduced alcohol intake at the time point of 24 h on the first treatment day. sCT reduced alcohol preference at the time point of c 1 h on treatment days 1 and 2 and at the time point of d 24 h on treatment day 1. sCT increased water intake at the time point of e 1 h on treatment day 1, but reduced water intake on treatment day 3 when compared to vehicle. At f 24 h, the sCT group showed increased water intake only on the first treatment day. Repeated sCT injections decreased total fluid intake at the time point of g 1 h on the first treatment day, but decreased water intake on the and last treatment day when compared to vehicle. sCT administration had no effect on water at the time point of h 24 h on any treatment day. sCT increased i 24-hour water intake during the untreated days when compared to vehicle. Repeated sCT injections (5 μg/kg, IP) decreased food intake in rats at the time point of j 1 h and k 24 h on all treatment days when compared to vehicle. l Repeated sCT administration increased the 24-hour values of percentage of body weight change. (Data are presented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; white circle indicates vehicle, black circle indicates sCT)