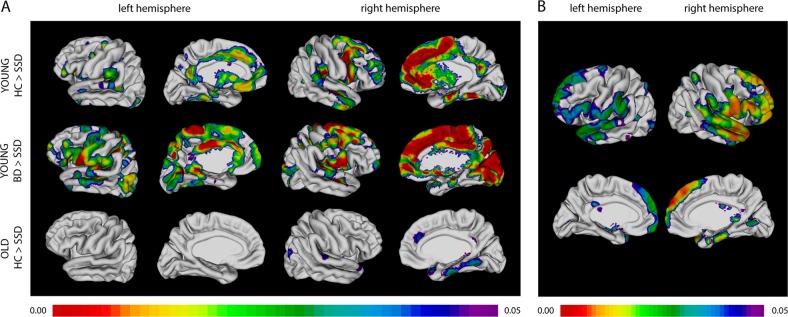
Fig. 2.
a Significant post hoc differences in cortical thickness between diagnostic groups after controlling for sex and parental education. b Cortical thickness is positively associated with PC1 scores after controlling for sex, parental education, and age. a In younger subjects, schizophrenia participants show reduced cortical thickness compared with those with BD and HCs in fronto-temporal cortex, and cortical midline regions. In older subjects, schizophrenia participants show reduced cortical thickness compared to HCs again in fronto-temporal regions. Only significant results are shown: no differences between the HCs and BD groups were found. b The entire sample (comprising HCs and participants with schizophrenia or BD) was included in this analysis. Associations of cortical thickness with PC1 score from the neurocognitive battery demonstrating associations with superior and inferior frontal, superior, middle, and inferior temporal regions, and the inferior parietal lobule. Legend. Diagnoses: HC = healthy control, SSD = schizophrenia spectrum disorder, BD = bipolar disorder. Age groups: young < 50 years, old ≥ 50 years. The color scale shows FDR-corrected p values < 0.05