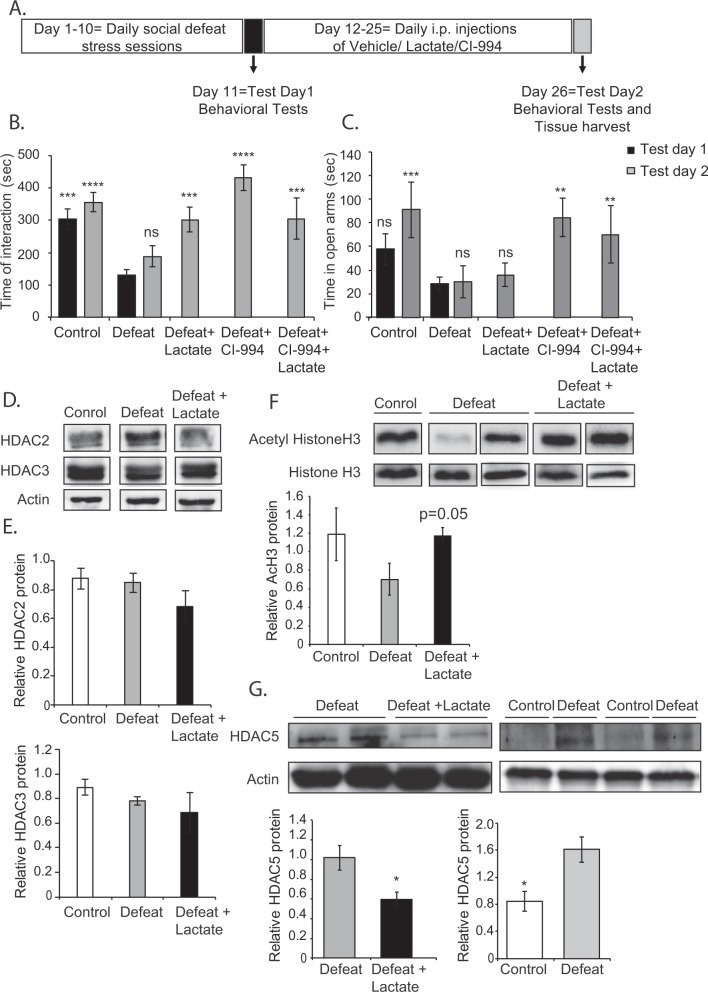
Fig. 5.
Lactate is an antidepressant that can rescue social avoidance phenotypes after their establishment. As an antidepressant, lactate increases hippocampal acetyl histone H3 and decreases hippocampal HDAC5 protein levels. a Modified chronic social defeat paradigm to assess the therapeutic potential of the compounds. This paradigm comprises of 10 days of daily defeat sessions that involve direct physical contact with an aggressor mouse for 7 min. On day 11, behavioral tests (test day 1) are conducted. During the 10 days of CSDS, mice do not receive any compound. From days 12–25, mice receive daily intra-peritoneal injections of either vehicle, lactate (180 mg/kg), CI-994 (30 mg/kg) or lactate + CI-994. On day 26, behavioral tests (test day 2) are conducted and tissue is collected. b Lactate rescues established defeat/depressed phenotype. Mice continue to exhibit social avoidance phenotype on test day 2 (day 26). No significant change is observed in the time of interaction between defeat groups on test day 1 and 2 (p = 0.8249). Intra-peritoneal injections of lactate (180 mg/kg), CI-994 (30 mg/kg), and lactate + CI-994, daily from days 12–25 reverse the chronic social defeat phenotype as shown by the significant increase on test day 2 in the time spent in interaction zone of the social interaction test as compared to the time spent there by the defeat group (test day 1 and 2). Statistical significance was measured by one-way Anova followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (F6,70 = 13.01, p < 0.0001). Significance was measured vs. the defeat groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ****p < 0.0001. The n numbers for the control (test day 1), control (test day 2), defeat (test day 1), defeat (test day 2), defeat + lactate (test day 2), defeat + CI-994 (test day 2), and defeat + lactate + CI-994 (test day 2) are 8, 8, 30, 6, 8, 8, and 8, respectively. c Lactate fails to rescue the established anxiety phenotype. Mice continue to exhibit anxious behavior on test day 2 (day 26). No significant change is observed in the time spent exploring the open arms of the EPM between defeat groups on test day 1 and 2 (p = 0.9998). Daily intra-peritoneal injections of lactate (180 mg/kg) from days 12–25 failed to rescue anxiety phenotypes; on the other hand, intra-peritoneal injections CI-994 (30 mg/Kg) were anxiolytic as shown by the significant increase on test day 2 in the time spent exploring the open arms of the EPM compared to the time spent there by the defeat group (test day 1 and 2). The combined treatment of lactate and CI-994 also significantly rescued anxiety. Statistical significance was measured by one-way Anova followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (F6,59 = 5.49, p = 0.0001). Significance was measured vs. the defeat groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ****p < 0.0001. The n numbers for the control, defeat, defeat + lactate, defeat + CI-994, and defeat + lactate + CI-994 are 5, 21, 6, 5, and 5, respectively. d Representative western blot images depicting hippocampal HDAC2 and HDAC3 levels in control, defeat, and defeat group receiving lactate from days 12–25. e Quantification of the HDAC2 and HDAC3 western blots. Statistical significance was measured by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-test. The n number of hippocampi analyzed is 4. f Representative western blot image depicting hippocampal acetyl histone H3 levels in control, defeat, and defeat group receiving lactate from days 12–25. Quantification of the acetyl histone H3 western blots. Statistical significance was measured by unpaired t-test. The n number of hippocampi analyzed is 4. g Representative western blot images depicting hippocampal HDAC5 levels in control, defeat, and defeat group receiving lactate from days 12–25. Quantification of the HDAC5 western blots. Statistical significance was measured by unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05. The n number of hippocampi analyzed is 3 for the control, 6 for the defeat group, and 5 for the defeat + lactate group