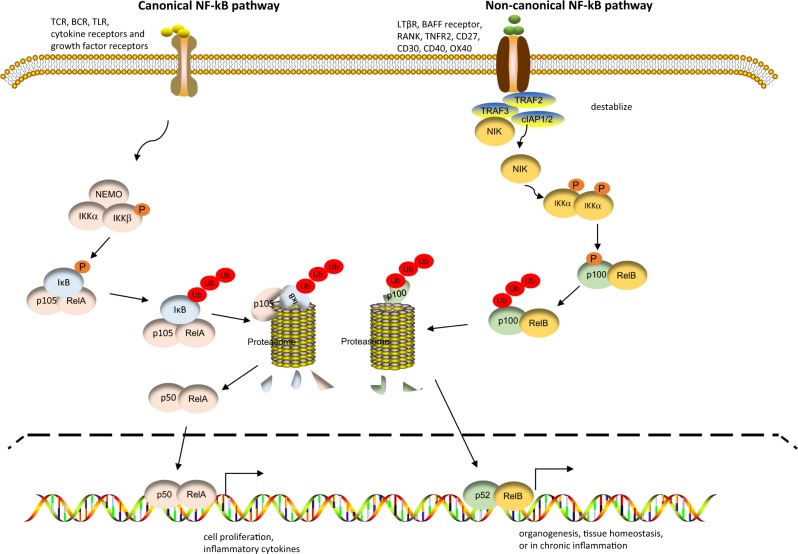
Fig. 2.
Pathways of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) activation. Activation of the canonical NF-κB pathway depends on the IKK complex, which consists of IKKα, IKKβ, and NEMO. Activated IKK phosphorylates the NF-κB inhibitor IκB, resulting in IκB degradation, which releases RelA and p105. Upon proteolytic cleavage of p105 to p50, RelA forms heterodimers with p50, and these RelA/p50 heterodimers translocate to the nucleus, where they bind and activate target genes. Activation of the noncanonical NF-κB pathway requires the induction of NIK in the cytosol. NIK associates with and activates IKKα, which phosphorylates p100, resulting in the proteolytic cleavage of p100 to generate p52. Then, p52 forms a heterodimer with RelB, and this RelB/p52 complex translocates to the nucleus to activate its target genes