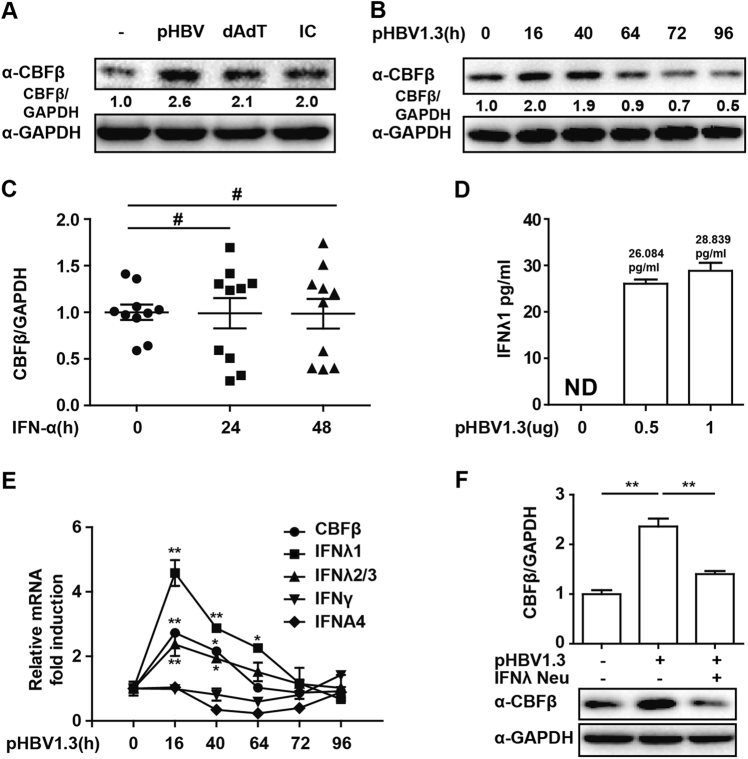
Fig. 1. CBFβ induction in the early stage of HBV infection.
a HepG2 cells were transfected with pHBV1.3 plasmids, polydAdT or polyIC, as indicated; 16 h later, whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with CBFβ or GAPDH antibodies. b HepG2 cells were transfected with pHBV1.3 plasmids, and cells were collected at different time points as indicated; whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting as in a. c PBMCs from HBV patients before or after IFN treatment were isolated and subjected to RNA extraction, and Q-PCR was performed to evaluate the CBFβ mRNA level. d HepG2 cells were transfected with pHBV1.3 plasmids as indicated. Then, 72 h later, supernatants were collected, and IFN-λ1 was analyzed by ELISA. e HepG2 cells were transfected as in b. Cells were collected and subjected to RNA extraction and Q-PCR analysis to measure CBFβ, IFN-λ1/2/3, IFN-γ, and IFNA4 expression. f HepG2 cells were transfected with pHBV1.3 plasmids and treated with IFN-λ1-neutralizing antibody as indicated; a western blot and Q-PCR were performed to evaluate the CBFβ level. All of the data are from three pooled independent experiments and are shown as the mean ± s.d. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, #p > 0.05