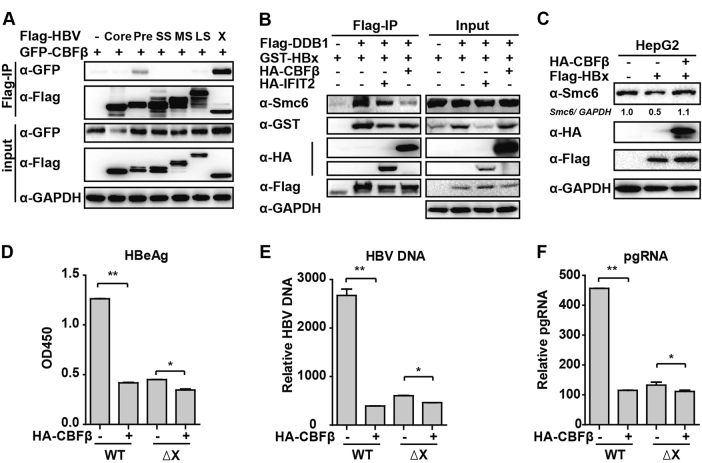
Fig. 6. CBFβ inhibits HBV replication through interacting with HBx.
a 293T cells were transfected with CBFβ or cotransfected with CBFβ and HBV protein expression plasmids as indicated; 24 h later, cells were collected and subjected to Co-IP assay, and the blot was immunoblotted with antibodies as indicated. b 293T cells were transfected with HA-CBFβ, HA-IFIT2, Flag-DDB1, or GST-HBx expression plasmids as indicated. Then, 32 h later, cells were collected and subjected to Co-IP assay, and the blot was immunoblotted with antibodies as indicated. (c) HepG2 cells were transfected with HA-CBFβ or Flag-HBx expression plasmids as indicated; 48 h later, cells were collected and subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies as indicated. d–f HepG2 cells were transfected with pHBV1.2 WT or pHBV 1.2ΔX plasmids, and with or without CBFβ as indicated. At 72 h, RNA and HBV DNA were isolated from the cells or supernatants and analyzed by Q-PCR. HBeAg in the supernatant was analyzed by ELISA. Data are presented as the means and s.d from three independent experiments. Student’s t-test was performed. *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01