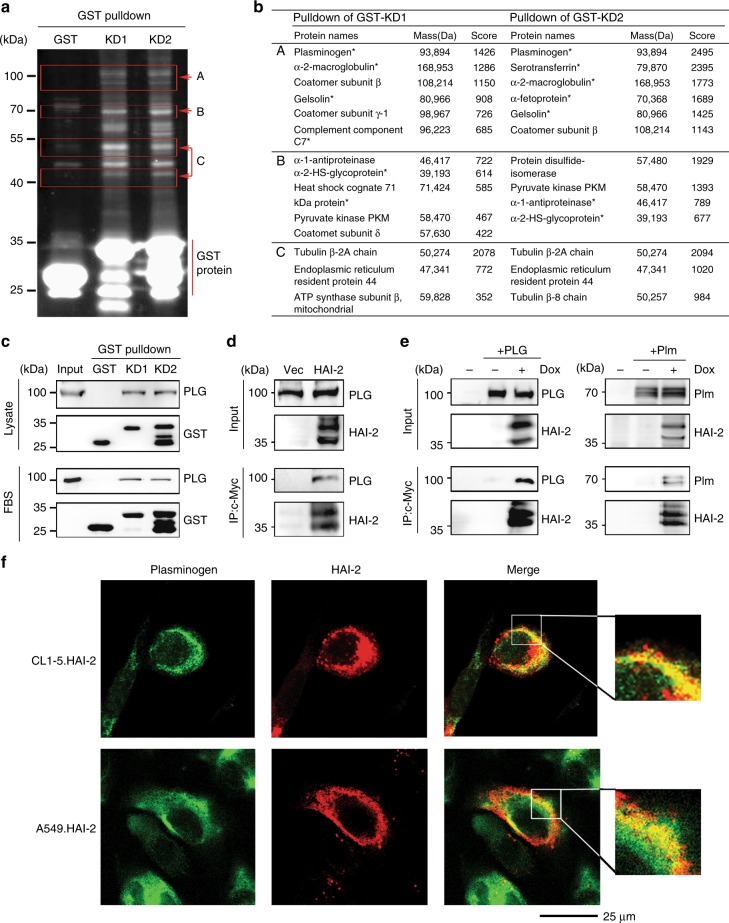
Fig. 3.
Identification of HAI-2’s associated proteins in lung cancer cells. a SYPRO Ruby-stained image of HAI-2’s associated proteins in an acrylamide gel after GST-pulldown and SDS-PAGE assays. The signals were captured by a UVP transilluminator. b The identity list of GST-pulldown proteins in (a) after LC-MS/MS analysis. c Immunoblot analyses of plasminogen after GST-HAI-2’s KD pulldown assays using CL1-5 cell lysate and FBS. d Co-immunoprecipitation of HAI-2 and plasminogen in HAI-2-overexpressing CL1-5 cells. HAI-2 proteins were pulled down from cell lysates by anti-c-Myc mAb (9E10). e Interaction of HAI-2 with plasminogen and plasmin using co-immunoprecipitation assays. A549 cells were transduced to carry a HAI-2.tet.aOn gene for HAI-2 overexpression upon doxycycline (Dox) induction. HAI-2 proteins were pulled down by anti-c-Myc mAb (9E10). The eluted samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-PLG and anti-HAI-2 pAbs. f Subcellular localisation of plasminogen and HAI-2 using confocal microscopy. The cells were cultured on cell culture slides and immunocytochemically stained with anti-PLG pAb and anti-HAI-2 mAb (DC16), followed by secondary antibodies (Alexa Fluor 488 and 568) incubation. The images were captured by a confocal microscope