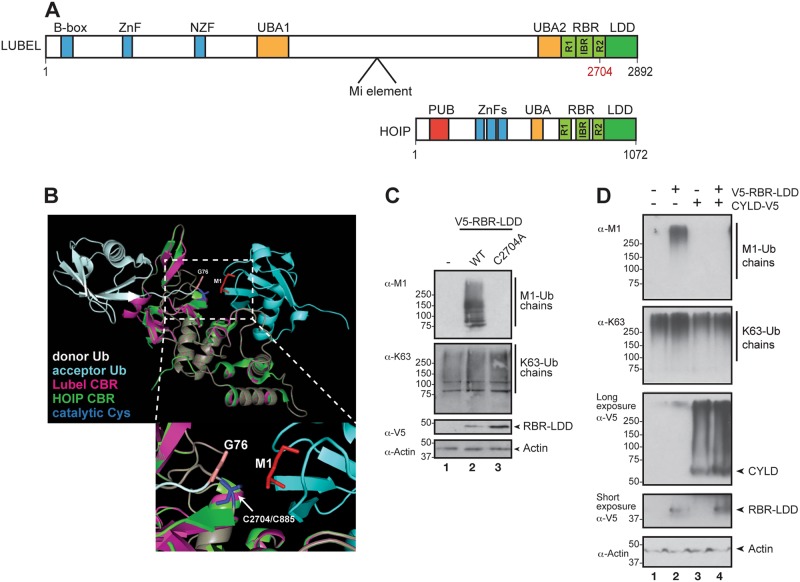
Fig. 2.
LUBEL synthesises and CYLD breaks down M1-Ub chains. a Schematic comparison of the different domains of LUBEL encoded by the lubel (CG11321) gene and human HOIP. The indicated cysteine residue marks the ubiquitin acceptor site in RING2. The lubelMi fly line carries a 7.5 kb Minos transposable element (Mi element) inserted between UBA1 and UBA2 in the lubel gene, as indicated in the figure (B-box, ZnF and NZF: zinc fingers; UBA: ubiquitin-associated domain; R: RING, really interesting new gene; IBR: in-between-RING; RBR: RING-in-between-RING; LDD: linear ubiquitin chain determining domain; PUB: peptide N-glycanase/UBA-containing or UBX-containing protein). b Structural modelling of the catalytic in-between-RING (CBR) consisting of RING2 and the LDD of LUBEL (Phyre2). The CBR of LUBEL (magenta) is modelled on human HOIP (green) associated with donor (white) and acceptor (light blue) ubiquitins (PDB: 4LJO). The catalytic cysteines are indicated in blue (LUBEL: C2704, HOIP: C885), the donor C-terminal glycines are shown in beige, while the acceptor M1 is shown in red. The lower panel is a zoom-in of the catalytic site in the upper panel. c Drosophila S2 cells were transfected with empty vector, V5-tagged wild-type or catalytically inactive C2704A mutant LUBEL RBR-LDD and lysates were analysed by Western blotting using α-M1, α-K63, α-V5 and α-Actin antibodies, n = 3. d Drosophila S2 cells were transfected with empty vector, V5-tagged wild-type LUBEL RBR-LDD and V5-tagged Drosophila CYLD and lysates were analysed by Western blotting with α-M1, α-K63, α-V5 and α-Actin antibodies, n = 3