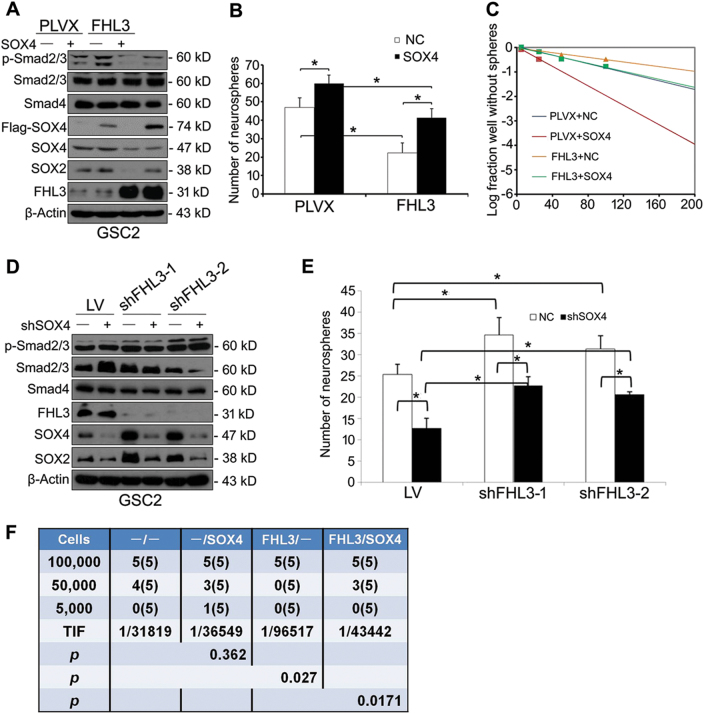
Fig. 7.
SOX4 rescues FHL3-mediated inhibition of SOX2 (stemness marker) expression and sphere-forming ability in glioma stem cells. a Following infection with PLVX vector or PLVX-FHL3 lentivirus, GSC2 cells were re-infected with control or Flag-SOX4 lentivirus. Representative western blot showing expression of FHL3 and Smad2/3–SOX4–SOX2 axis-related proteins in the infected GSC2 cells. b Sphere formation assay in the infected GSC2 cells. c Limiting dilution neurosphere assay in the infected GSC2 cells. d Following infection with control shRNA lentivirus (LV) or shFHL3 lentivirus (shFHL3-1 and shFHL3-2), GSC2 cells were re-infected with control or shSOX4 lentivirus. Representative western blot showing expression levels of Smad2/3–SOX4–SOX2 axis-related proteins and FHL3 in the infected GSC2 cells. e Sphere formation assay in the shRNA lentivirus-infected GSC2 cells. f Limiting dilution assay showing rescue of GSC2 tumor-initiating capacity by SOX4 in vivo. Limiting dilutions of the infected GSC2 cells were subcutaneously implanted into nude mice. The table shows the number of mice that grew tumors at week 10 (out of a total of 5 mice per group). Tumor-initiating frequency (TIF) was calculated using ELDA software. P < 0.05 was used as the significance threshold for comparisons between the FHL3-overexpression group and the control group as well as the FHL3 and SOX4 co-overexpression group and the FHL3-overexpression group. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05