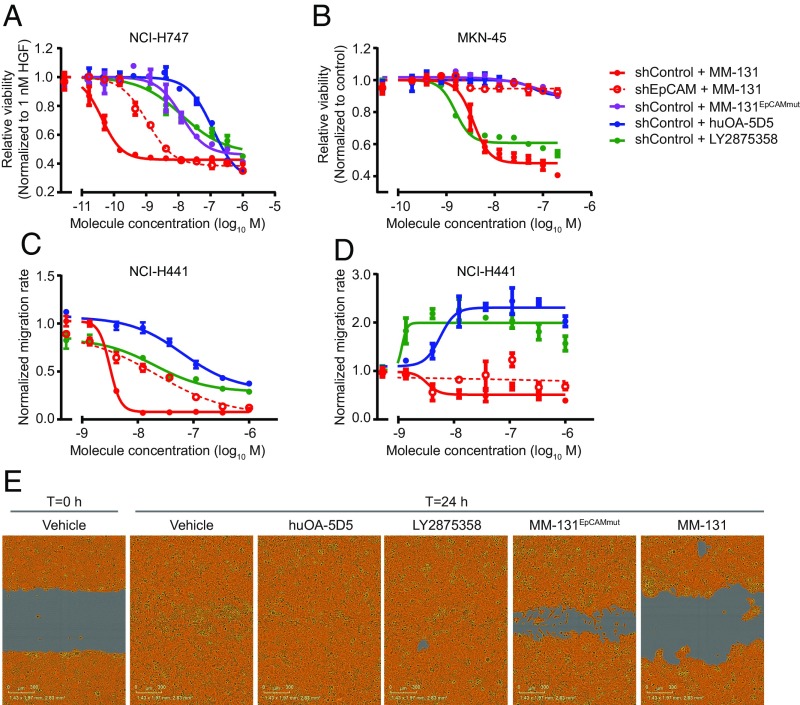
Fig. 4.
MM-131 inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration. MM-131 blocks HGF-dependent cell proliferation (A) and proliferation of MET-amplified cells (B) in a dose-dependent manner. NCI-H747, NCI-H441, and MKN-45 cell lines were stably transduced with lentiviral particles expressing untargeted shRNA (shControl) or shRNA targeting EpCAM (shEpCAM). Following formation of 3D spheroids, cells were treated with the indicated antibodies for 96 h. Viability was assessed by CellTiter-Glo assay and normalized to vehicle-treated cells in the presence (A) or absence (B) of 1 nM HGF. (C) MM-131 blocks HGF-induced cell migration in a dose-dependent manner. Following production of a uniform scratch wound, images were taken every 2 h for 24 h. Migration rates were calculated from the relative wound densities (density of cells inside the wound area/density outside the wound area) of each image and normalized to vehicle-treated cells in the presence of 1 nM HGF. (D) Unlike huOA-5D5 and LY2875358, MM-131 does not promote migration in the absence of HGF. A scratch wound migration assay was performed as in C, except in the absence of HGF. Migration rates were normalized to vehicle-treated cells in the absence of HGF. (E) Representative images of NCI-H441 cells from an HGF-induced migration assay. Images are from 1 μM treatment of indicated molecules. The wound area remaining is shown in gray, and the confluence mask is shown in orange. All plots reflect mean (n = 3) and SEM.