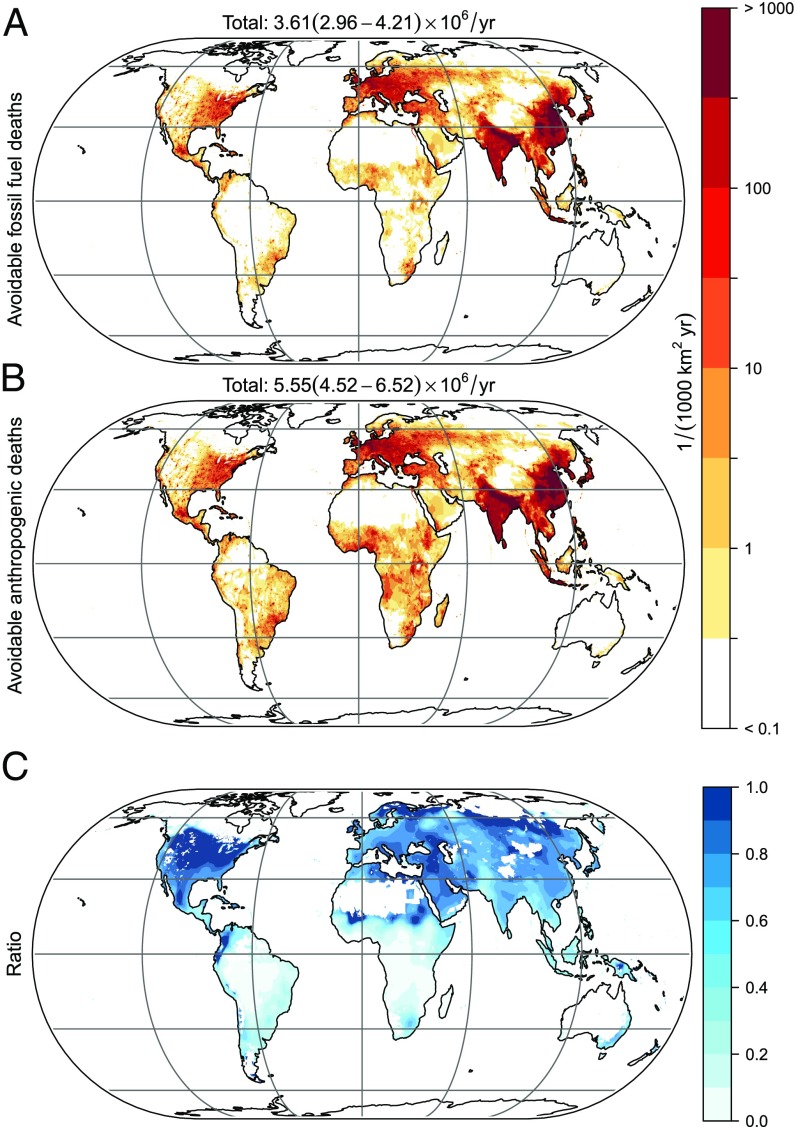
Fig. 1.
Avoidable excess mortality rate from air pollution. Units: deaths per 1,000 km2/y. (A) Excess deaths that may be avoided by the phasing out of fossil fuels, and (B) by all anthropogenic emissions. (C) Relative contribution to excess deaths from fossil fuel use compared with all anthropogenic emissions. The dark-blue regions would profit more from removing fossil-fuel-related emissions, while the light-blue ones profit more from removing other pollution sources.