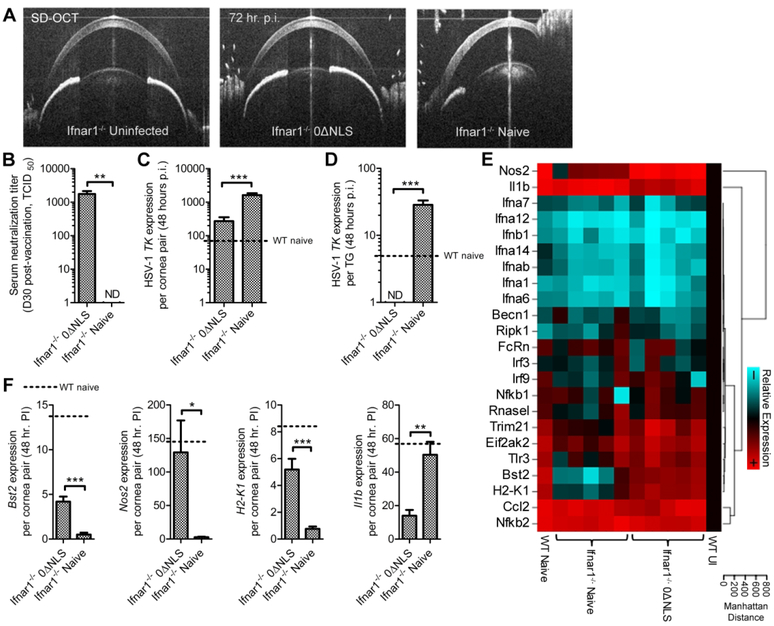
Fig. 3. Contributions of type 1 interferon signaling to prophylactic protection.
Type 1 interferon (IFNα/β) receptor-deficient (Ifnar1−/−) mice were prophylactically vaccinated in the footpad with 1×105 plaque forming units (PFU) of HSV-1 0ΔNLS and ocularly challenged 30 days later with 1×105 PFU HSV-1 McKrae per eye. (A) Spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) imaging of the anterior eye of Ifnar1−/− animals 72 hours p.i. (B) Serum neutralizing titers in vaccinated and naive Ifnar1−/− mice. Relative expression of HSV-1 thymidine kinase (TK) in the cornea (C) and trigeminal ganglia (D) of Ifnar1−/− mice at 48 hours post-infection (p.i.). Expression data was normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression and relative to tissue from uninfected WT C57BL/6 mice. (E) Heat map of antiviral gene expression at 48 hours p.i. generated using Biorad PrimePCR technology and the National Cancer Institute’s online Cluster Image Map tool (http://discover.nci.nih.gov/cimminer/). Host gene expression was relative to the geometric mean of beta actin, GAPDH, and phosphoglycerokinase 1 expression and normalized to tissue from uninfected WT C57BL/6 mice. Data sets in which significant differences (Student’s T tests) were identified in host gene expression between naive and vaccinated Ifnar1−/− mice are shown in (F). Data in each panel reflect the summary of n = 5 mice/group with two independent experiments. Gene expression levels detected in HSV-infected WT mice are depicted for reference in panels C,D, and F. Abbreviations: TCID50, median tissue culture infectious dose; ND, not detected; WT, wild-type; Nos2, inducible nitric oxide synthase; Il1b, interleukin 1β, Ifn, interferon; Becn1, beclin1; Ripk1, receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; FcRn, neonatal Fc receptor; Irf, interferon regulatory factor; Nfkb, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Rnasel, ribonuclease L; Trim21, tripartite motif-containing protein 21; Eif2ak2, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 2; Bst2, bone-marrow stromal antigen 2 (tetherin); Tlr, Toll-like receptor; H2-K1, histocompatibility 2, K1 region (MHC class I); Ccl2, c-c motif chemokine ligand 2.