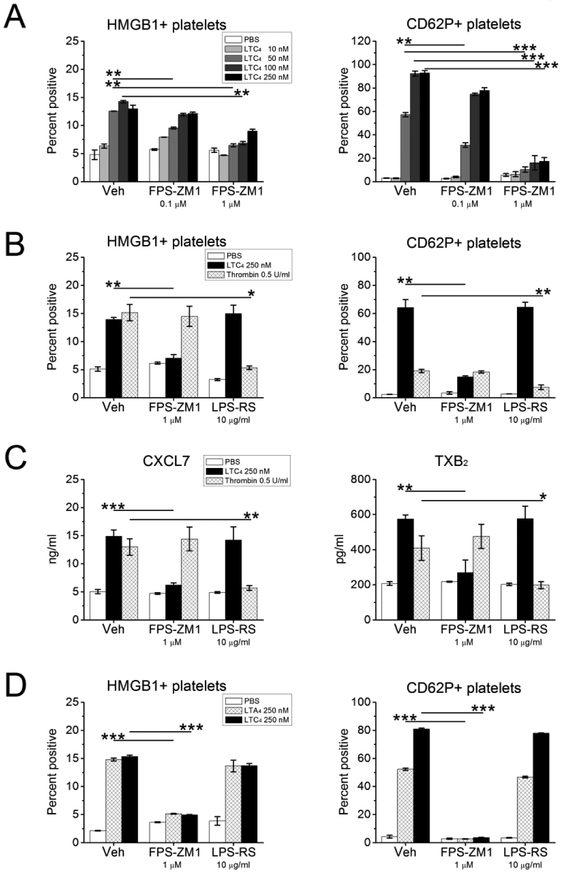
Figure 2. Effects of RAGE or TLR4 blockade on LTC4-induced platelet activation.
PRP was obtained from the indicated mouse strains and stimulated with LTC4 at the indicated concentrations or with thrombin (0.5 U/ml). Some samples were treated with the selective RAGE antagonist FPS-ZM1, and others with the TLR4 antagonist LPS-RS at the indicated doses prior to stimulation. A. Effects of RAGE blockade on LTC4induced surface expression of HMGB1 (left) and CD62P (right) by CD41+ platelets stimulated for 30 min. B. Effects of RAGE and TLR4 blockade on expression of HMGB1 (left) and CD62P (right) by platelets in PRP stimulated for 30 min by LTC4 or thrombin. C. Concentrations of CXCL7 (left) and TXB2 (right) detected by ELISA in the supernatants from PRP stimulated as in B. D. Effects of RAGE and TLR4 antagonists on surface expression of HMGB1 (left) and CD62P (right) by platelets in PRP stimulated by LTA4 (to elicit conversion by platelet LTC4S) or LTC4 at the indicated doses. Results in A-D are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments that included a minimum of 3 mice per group.