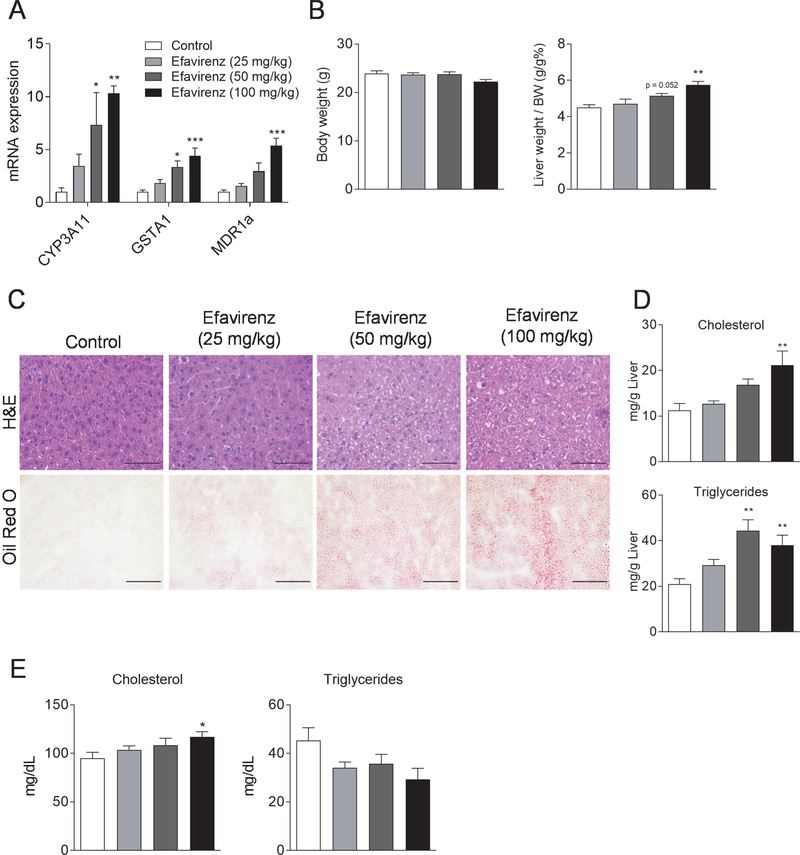
Figure 2. Exposure to efavirenz induces hypercholesterolemia and liver steatosis in wild-type mice.
Eight-week-old male WT mice were treated with vehicle, 25, 50, or 100 mg/kg/day of efavirenz by oral gavage for 1 week. (A) QPCR analysis of the hepatic expression of PXR target genes. (B) Body weight and the ratio of liver weight to body weight. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin (top, bar=50 μm) and Oil red O (bottom, bar=100 μm) stained liver sections. (D) Hepatic total cholesterol and triglyceride levels. (E) Plasma total cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA (A, B, D, and E). (n=5–6, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 compared to control group).