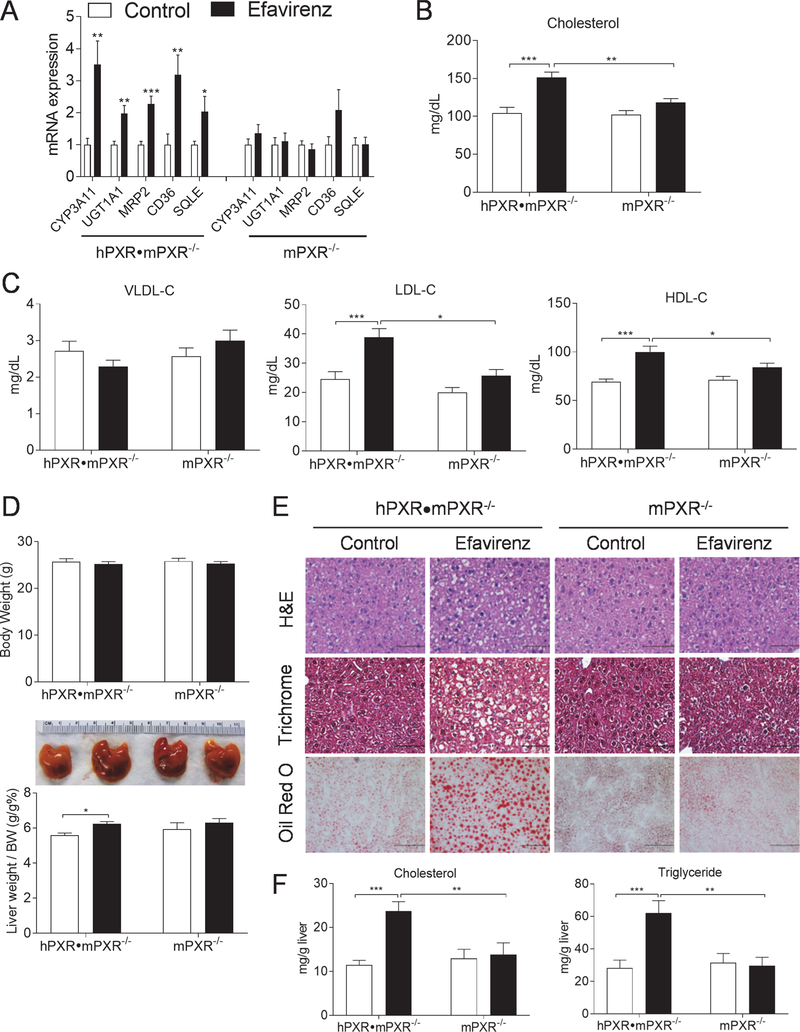
Figure 7. Efavirenz induces hypercholesterolemia and hepatic steatosis in PXR-humanized mice.
Eight-week-old male hPXR•mPXR−/− and mPXR−/− littermates were treated with vehicle control or 100 mg/kg/day of efavirenz for 1 week. (A) QPCR analysis of hepatic gene expression. (B and C) Plasma total cholesterol (B) and VLDL, LDL, and HDL cholesterol levels (C). (D) Body weight, the ratio of liver weight to body weight, and representative liver image. (E) Representative H&E (bar=50 μm), Trichrome (bar=50 μm), and Oil red O (bar=100 μm) stained liver sections. (F) Hepatic total cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Significance was determined by Student’s t test (A) or two-way ANOVA (B-D, and F). (n=5–7, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001).