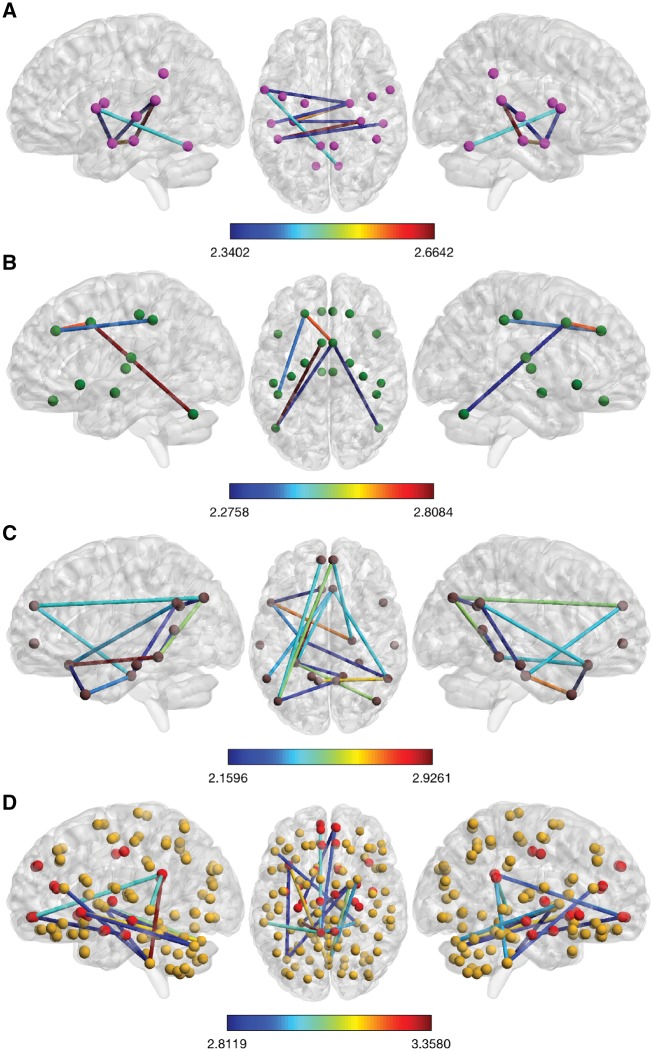
Figure 1.
Takotsubo syndrome-related hypoconnectivity among central nervous brain structures controlling para- and sympathetic functions as well as regions associated with the default mode network and limbic system. Shown are the more conservatively thresholded subnetworks with reduced resting state functional connectivity in Takotsubo syndrome patients compared with healthy control women. Colour bars represent the set t-value of the connections between which the two groups differ in connectivity strength. The more liberally thresholded subnetworks and detailed information of the nodes and connections involved are shown in the Supplementary materials online. (A) At the higher set threshold (t = 2.30), the Takotsubo syndrome-related parasympathetic-associated hypoconnected subnetwork is composed of seven edges distributed over eight nodes (P = 0.003, FWE-corrected, 5000 permutations). A detailed description of the nodes constituting the subnetworks can be found in Supplementary material online, Table S3. Among these nodes are the right amygdala, left and right hippocampus, left and right middle and superior temporal gyrus, left primary motor cortex and the left supramarginal/angular gyrus, and the left cerebellum. (B) At the higher set threshold (t = 2.25), the Takotsubo syndrome-related sympathetic-associated hypoconnected subnetwork is composed of five edges distributed over six nodes (P = 0.044, FWE-corrected, 5000 permutations). A detailed description of the nodes constituting the subnetworks can be found in Supplementary material online, Table S4. Among these nodes are the left and right amygdala, left and right middle cingulate gyrus, left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, left anterior insular cortex, left and right cerebellum, and left and right supramarginal gyrus and superior parietal lobule. (C) At the higher set threshold (t = 2.15), the Takotsubo syndrome-related hypoconnected default mode network is composed of 15 edges distributed over 15 nodes (P = 0.033, FWE-corrected, 5000 permutations). A detailed description of the nodes constituting the subnetworks is depicted in Supplementary material online, Table S5. Among these nodes are the left and right hippocampus, left parahippocampal gyrus, left and right dorsal and ventral medial prefrontal cortex, left posterior cingulate cortex, left temporal pole, left and right inferior parietal lobule, and the left and right temporoparietal junction. (D) At the higher set threshold (t = 2.80), the Takotsubo syndrome-related hypoconnected subnetwork is composed of 13 edges distributed over 13 nodes (P = 0.023, FWE-corrected, 5000 permutations). A detailed description of the nodes constituting the subnetworks is depicted in Supplementary material online, Table S6. Among these nodes are the left anterior insular cortex, left posterior cingulate cortex, left and right medial orbitofrontal cortex, left middle temporal gyrus, right pallidum, and the cerebellum.