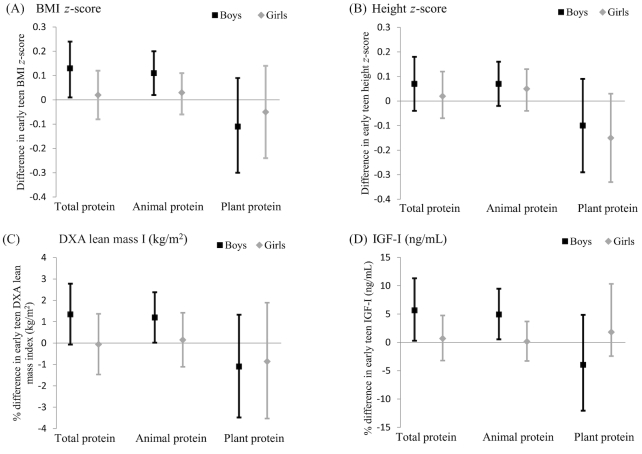
FIGURE 2.
Associations of total, animal, and plant protein intake in early childhood with BMI z score (A), height z score (B), DXA lean mass index (kg/m2) (C), and IGF-I (ng/mL) (D) in early adolescence among Project Viva boys and girls. Points are βs (BMI z score and height z score) or percentage differences (DXA lean mass index and IGF-I), with 95% CIs represented by error bars. Results were generated from multivariable linear regression models adjusted for child race/ethnicity, child age at outcome measurement (except z score outcomes), child age at diet assessment, household income, maternal education, breastfeeding status at 6 mo, and: 1) maternal and paternal BMI, birth weight for gestational age z score, fast food intake, and physical activity (BMI z score); 2) fast food intake and physical activity (DXA lean mass index); or 3) maternal and paternal height and birth length (height z score and IGF-I). Protein intake is adjusted for total energy intake and body weight at the time of diet assessment. n = 963 for analyses of BMI z score, height z score, and DXA lean mass index; n = 717 for analyses of IGF-I. DXA, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; IGF-I, insulin-like growth factor I.