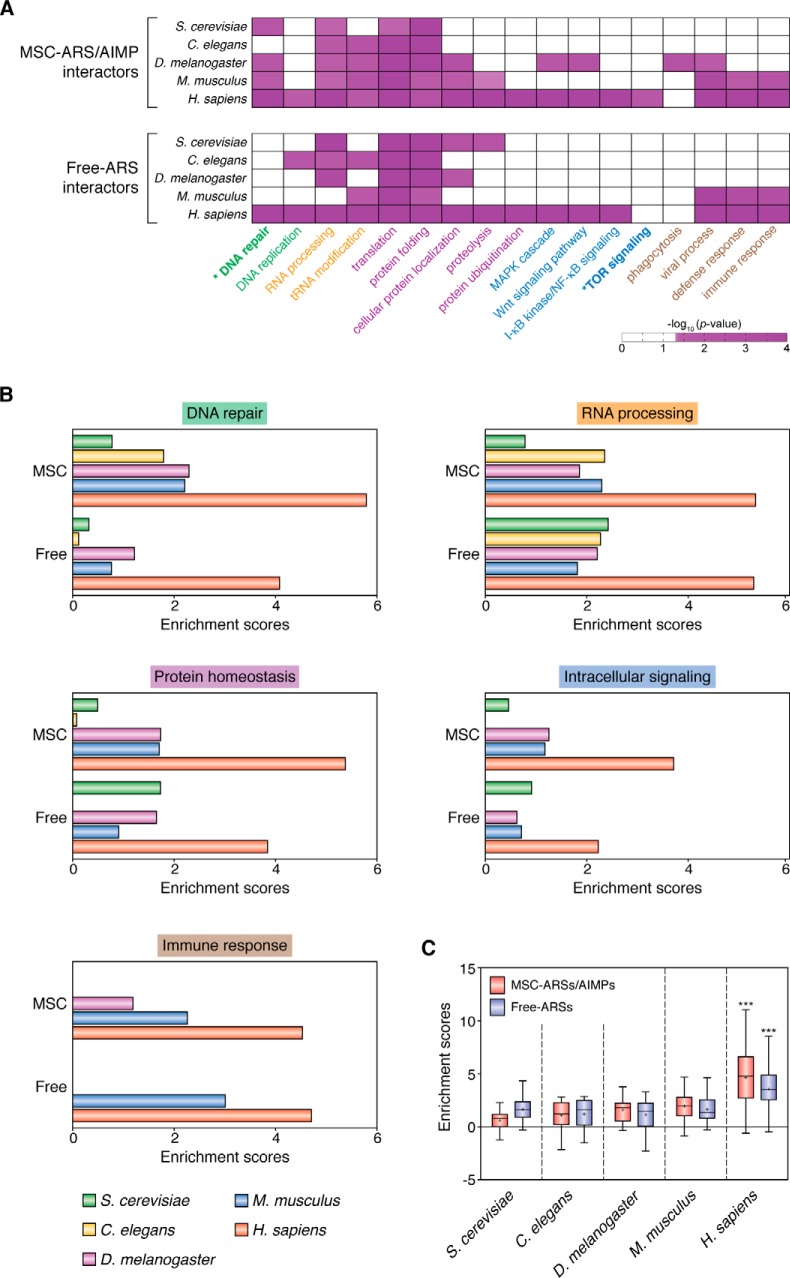
Figure 4.
Comparative functional enrichment analysis of ARS interactomes in five species. A, GOBPs enriched by the interactors of MSC–ARSs/AIMPs and free-ARSs in S. cerevisiae, C. elegans, D. melanogaster, M. musculus, and H. sapiens. The five enriched cellular processes are labeled in different colors: 1) DNA replication (DNA repair and replication; green); 2) RNA processing (tRNA modification and RNA processing; orange); 3) protein homeostasis (translation, protein localization, and proteolysis; purple); 4) intracellular signaling (Wnt, MAPK, mTOR, and NF-κB signaling; blue); and 5) immune response (defense response, phagocytosis, and viral process; brown). The color bar represents the gradient of −log10 (p value), where the p value is the significance of the GOBPs being enriched by the interactors, which was computed from DAVID software. For visualization, hierarchical clustering was performed for each group of cellular processes using Ward linkage and Euclidean distance as the similarity measure. B, enrichment scores of the indicated representative processes (DNA repair, RNA processing, protein localization–proteolysis, immune response–viral process, and intracellular signaling) for the five groups of cellular processes enriched by MSC–ARS/AIMP (top) and free-ARS interactors (bottom) in the five species. C, distributions of the enrichment scores of the representative processes by MSC–ARS/AIMP (pink) and free-ARS interactors (purple) in the five species are shown using box plots. Z >2.33, *, p < 0.05, and ***, p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-hoc correction. See supporting information for methodological details.