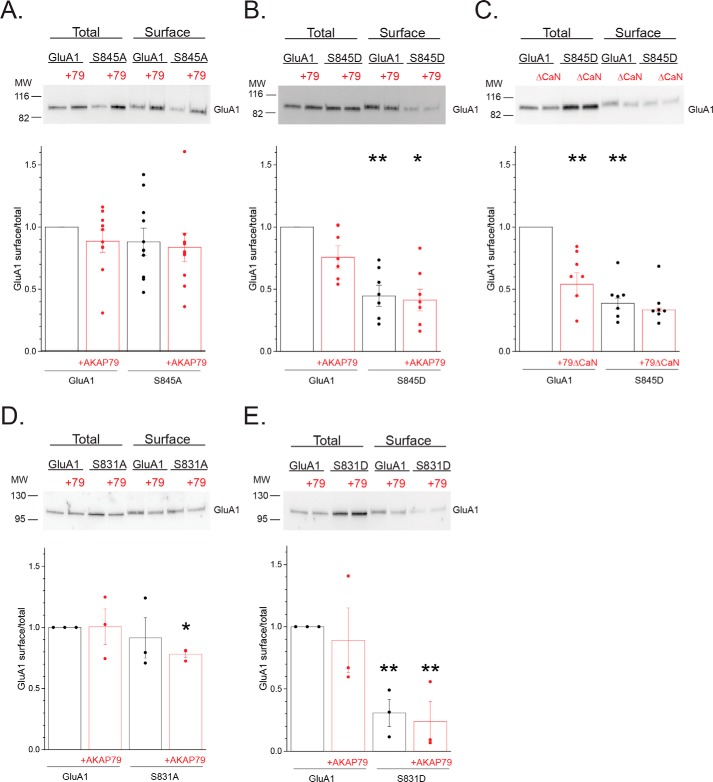
Figure 8.
Phosphorylation cycling regulates GluA1 surface expression. A, HEK 293 cells were transfected with GluA1 or S845A with or without AKAP79-mCherry and subjected to cell surface biotinylation, followed by immunoblot analysis for GluA1. Top, representative Western blotting. Bottom, summary graph quantifying the results from multiple experiments. Data are normalized to the surface/total ratio for GluA1 alone. Individual data points for each experiment are shown. B, similar analysis comparing the phosphomimetic S845D with WT GluA1, demonstrating that mimicking phosphorylation constrains surface expression of obligate homomers. **, p < 0.01, compared with GluA1; *, p < 0.05, compared with GluA1 + AKAP79. C, complementary experiment in which the CaN-deficient mutant was co-expressed with either GluA1 or the S845D mutant, suggesting that “overphosphorylation” of WT GluA1 similarly impairs surface expression. **, p < 0.01, compared with GluA1; *, p < 0.05, compared with GluA1 + AKAP79ΔCaN. D and E, parallel analysis examining the impact of phosphodeficient S831A (D) and the phosphomimetic S831D (E) mutations on the surface expression of obligate GluA1 homomers. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, compared with GluA1.