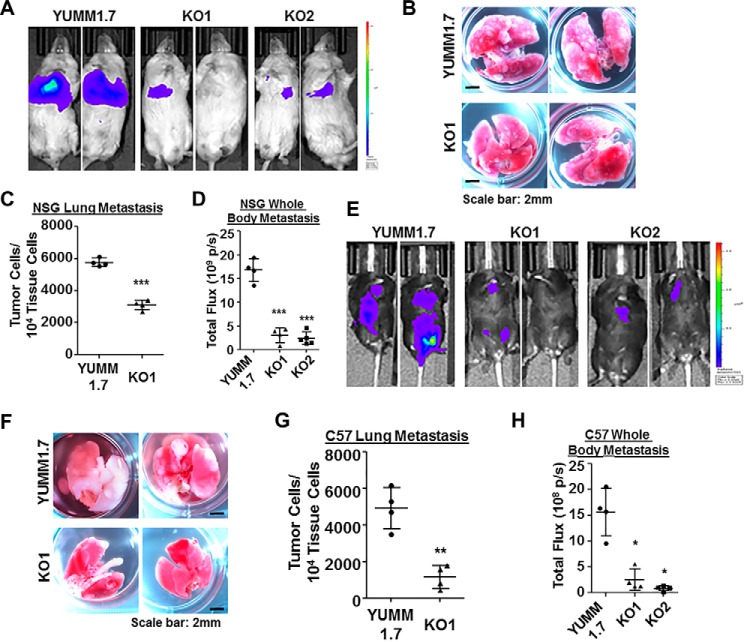
Figure 4.
Wisp1 knockout repressed the experimental metastasis of melanoma cell line YUMM1.7 in NSG and C57BL/6Ncrl mice. Experimental metastasis assays were performed in NSG (A–D) and C57BL/6Ncrl (E–H) mice using YUMM1.7 and the indicated knockout cells with injection through mouse tail veins. Each group contained five duplicates (n = 5), and two representative images are shown. A, bioluminescence imaging performed 1 day before NSG mice were euthanized. All animals were compared with the same bioluminescence scale. B, tumor lung metastases (white nodules) of NSG mice as captured by photography. C, real-time genomic qPCR quantitatively comparing tumor lung metastatic burdens (tumor cell number within 10,000 mouse tissue cells). D, the whole-body metastasis of tumor cells in NSG mice was plotted and compared using bioluminescence intensity detected in A. Total flux is presented as photons/s (p/s). E, bioluminescence imaging performed 1 day before C57BL/6Ncrl mice were euthanized. All animals were compared with the same bioluminescence scale. F, tumor lung metastases (white nodules) of C57BL/6Ncrl mice as captured by photography. G, real-time genomic qPCR quantitatively comparing tumor lung metastatic burdens. H, whole-body metastasis of tumor cells in C57BL/6Ncrl mice was plotted and compared using bioluminescence intensity detected in E. Two high-resolution images for B and F are provided as Figs. S7 and S8. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. Error bars, S.D.