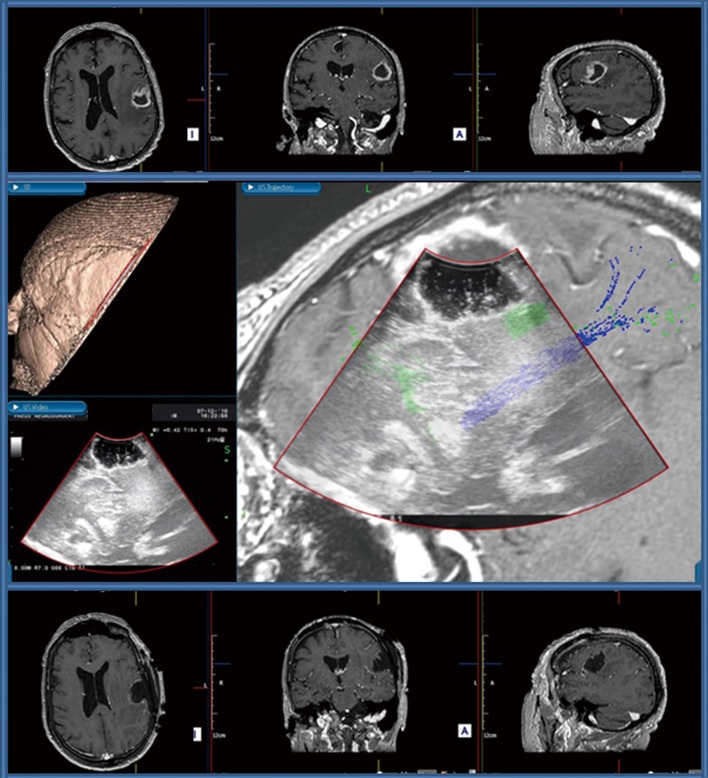
Figure 1.
Awake craniotomy for a left-sided motor strip glioma. Upper row: Preoperative post-contrast T1WI MRI scan showing an irregular cortico-subcortical lesion in the left frontal operculum, characterised by ill-defined peripheral gadolinium uptake and central necrosis with a significant amount of surrounding vasogenic edema. Central Image: Screenshot of image fusion created for neuronavigation purposes by coupling IoUS and preoperative MRI scan. Real-time visualisation of the relation of the surgical cavity with subcortical association fibres, note the green fibres seen adjacent to the deep aspect of the surgical cavity indicating the Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus and Inferior Fronto-Occipital Fasciculus serving speech function, and the blues fibers indicating the cortico-spinal tract. The presence of these fibres was confirmed with subcortical stimulation during the procedure. Bottom row: Postoperative post-contrast T1WI MRI scan showing a complete surgical resection with a clear surgical cavity.