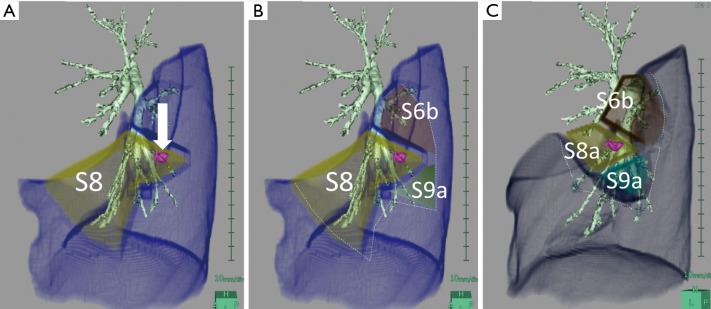
Figure 1.
Different extents of resection in anatomical segmentectomy for the same pulmonary lesion. An example of (A) conventional anatomical segmentectomy (the arrow indicates the tumor to be targeted); (B) extended segmentectomy; and (C) combined subsegmentectomy, for the same lesion located in left segment 8 (S8). Compared with conventional anatomical segmentectomy in which the resection may be “unbalanced,” extended segmentectomy and combined subsegmentectomy may provide better resection margins. This figure is cited from reference (8) with permission.