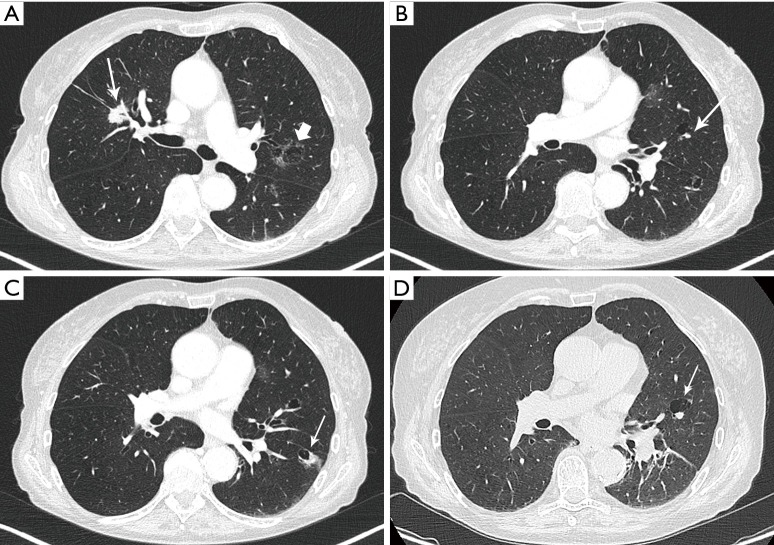
Figure 2.
Axial images in lung window setting in a 68-year-old woman who presented with numerous pulmonary nodules of variable morphology, including numerous lesions with cystic airspace morphology. (A) Histopathologic examination (transbronchial biopsy) of the spiculated solid nodule in the right upper lobe (thin white arrow) showed an invasive adenocarcinoma with EGFR exon 18 mutation. Also note a cystic airspace area in the left upper lobe, with interspersed areas of ground glass (thick white arrow); (B) in the left upper lobe there is a small cystic airspace with small exophytic solid nodule (white arrow); (C) in the left lower lobe there is a third cystic-airspace lesion, with focal asymmetric wall thickening and exophytic solid component with surrounding ground glass. Histopathologic examination of this lesion showed an adenocarcinoma with different histological morphology and molecular profile (no EGFR mutation) than the spiculated solid lesion in the right upper lobe; (D) during follow-up the exophytic nodule abutting the cystic airspace in the left upper lobe steadily increased in size. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor.