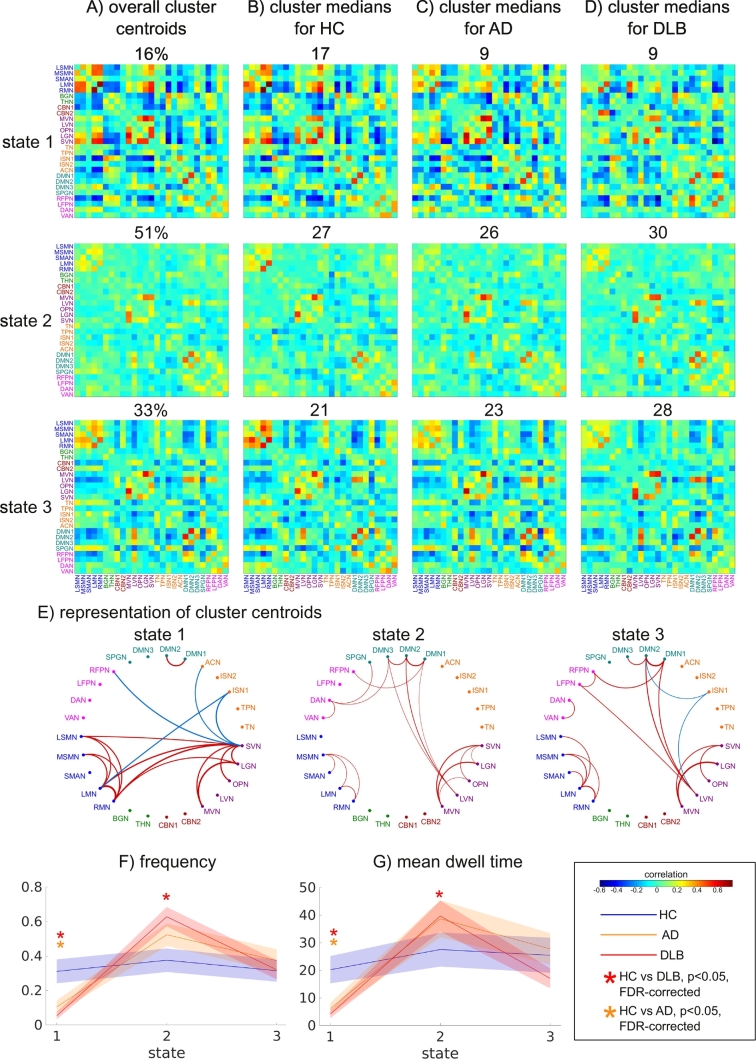
Fig. 4.
Results from k-means analysis. A) Centroids resulting from clustering on all windows with the overall percentage of windows assigned to the respective cluster (shown above each matrix). B) Cluster medians in the healthy control (HC) group and the number of HC patients expressing a state displayed above the respective matrix. C) Cluster medians in the Alzheimer's disease (AD) group and the number of AD patients expressing a state displayed above the respective matrix. D) Cluster medians in the DLB group and the number of DLB patients expressing a state displayed above the respective matrix. E) Network representation of cluster centroids showing only the 5% strongest positive (red) and negative (blue) connections. F) Comparison of frequency of occurrence between the three groups for each state, solid lines represent the means per group, shaded areas represent error bars of the standard error. G) Comparison of mean dwell time in each state between the three groups. FDR-corrected p-values<0.05 (from post-hoc tests) are marked with an asterisk.
LSMN, lateral sensorimotor network; MSMN, medial sensorimotor network; SMAN, supplementary motor network; LMN/RMN, left/right motor network; BGN, basal ganglia network; THN, thalamic network; CBN, cerebellar network; MVN, medial visual network; LVN, lateral visual network; SVN, superior visual network; TN, temporal network; TPN, temporal pole network; ISN, insular network; ACN, anterior cingulate network; DMN, default mode network; SPGN, supramarginal gyrus network; RFPN/LFPN, right/left fronto-parietal network; DAN, dorsal attention network; VAN, ventral attention network.