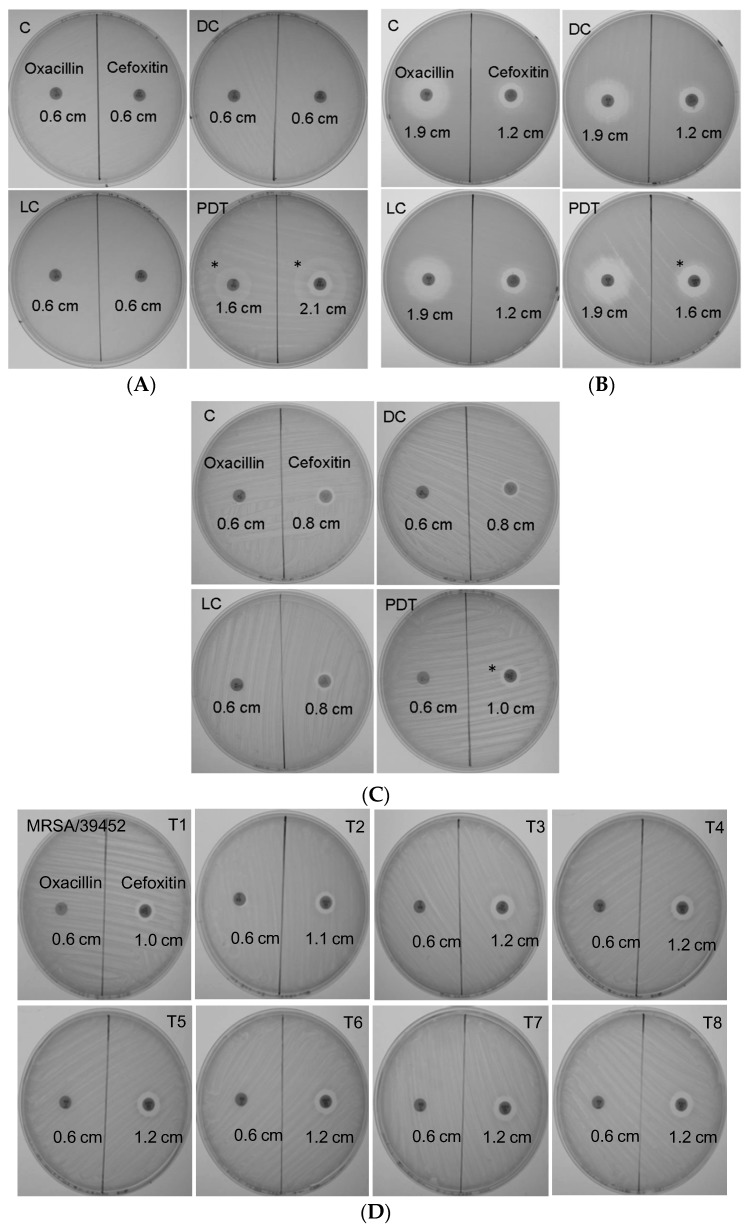
Figure 2.
Alterations in MRSA drug sensitivity after ICG-PDT. (A) MRSA/JD004, (B) MRSA/BAA-1556, and (C) MRSA/39452 were incubated with 25 µg/mL of ICG and exposed to 100 J/cm2 near-infrared at 65.5 mW/cm2; (D) MRSA/39452 was treated repeatedly with ICG-PDT up to eight times. The clear zones were created by MRSA growth inhibition by antibiotic in the disks. (A) In MRSA/JD004, the oxacillin inhibition zone increased from 0.6 to 1.6 cm after PDT (166.7% increment), and the cefoxitin inhibition zone increased from 0.6 to 2.1 cm (250% increment). (B) The oxacillin clear zone did not change in MRSA/BAA-1556, but the cefoxitin clear zone increased from 1.2 to 1.6 cm (33% increment, Figure 2B) after PDT. (C) In MRSA/39452, there was a small increase in the cefoxitin inhibition zone (0.8 to 1.0 cm; 25% increment) and no change in the oxacillin inhibition zone. (D) In MRSA/39452, the oxacillin diameter did not change after two more repeated treatments, yet the cefoxitin inhibition zone further increased by 20%. The changes of the drug-sensitivity phenotype were maintained until the eighth repeated PDT. T1–T8: number indicates the number of times exposed to PDT. MRSA that survived from the previous PDT treatment were used for the subsequent treatment. The above are representative data of three separate experiments. C: absolute control; DC: dark control; LC: light control; PDT: photodynamic therapy. * sensitive to oxacillin.