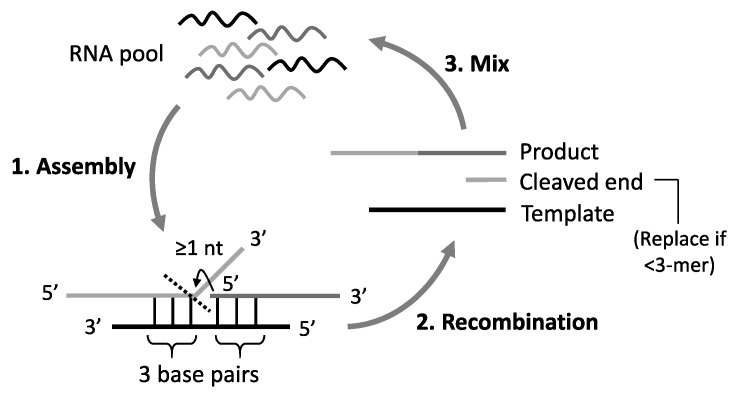
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the simulation under template-dependent recombination. (1) One template and two substrate RNAs were randomly chosen from an RNA population, and they assembled to form base pairs between the substrates and the template. (2) The substrates recombined if the complex satisfied the criteria described in the main text: E.g., three consecutive base pairs on either side of the recombination junction. The left-side substrate was cleaved at the nucleotide indicated by the dashed line and ligated with the right-side substrate. One recombination reaction generated a product, a cleaved end, and the template. (3) They were put back into the RNA population or replaced with an RNA in the initial population if their lengths were too short to react (<3-mer). This cycle was repeated up to a given number of reaction steps.