Figure 5.
Cdc42 Activation Is Critical for the Cell-to-Cell Spread of Oncolytic Vaccinia Virus-LG Induced by UCA1 Expression
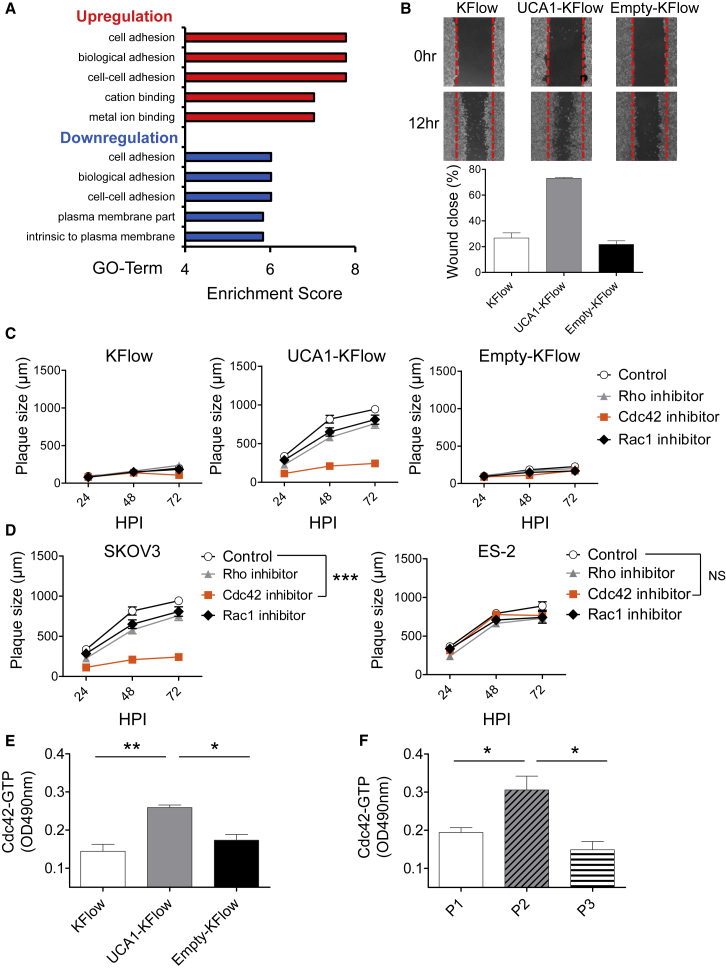
(A) Results of gene ontology analysis after microarray analysis. Gene lists correspond to 2-fold changes in KFlow and UCA1-KFlow cells. (B) A pipette tip was used to introduce a scratch in a monolayer of KFlow, UCA1-KFlow, and Empty-KFlow cells in the absence of serum. The percentage of wound closure was estimated using the analysis application measurement module (Keyence) (n = 6). (C and D) KFlow, UCA1-KFlow and Empty-KFlow (C) and SKOV3 and ES-2 cells (D) were treated with Rhosin (targeting Rho; 50 nM), ML-141 (targeting Cdc42; KFlow, UCA1-KFlow, and Empty-KFlow, 20 nM; SKOV3, 18 nM; ES-2, 15 nM), and NSC23766 (targeting Rac1; KFlow, UCA1-KFlow, Empty-KFlow, and SKOV3, 30 nM; ES-2, 15 nM) inhibitors and infected with OV-LG (MOI = 0.001). Representative plaques formed under semisolid medium were photographed and calculated with the analysis application measurement module (Keyence) (n = 10). (E and F) Activation of Cdc42 in KFlow, UCA1-KFlow and Empty-KFlow (E) and primary ovarian cancer cells (F) was analyzed by performing a colorimetric G-LISA assay (n = 3). Data with error bars represent mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA was used for (C) and (D).*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.