Figure EV2. Pull‐down assays measuring the active state of Rab7 do not show apparent changes in PI4K2A K/O cells.
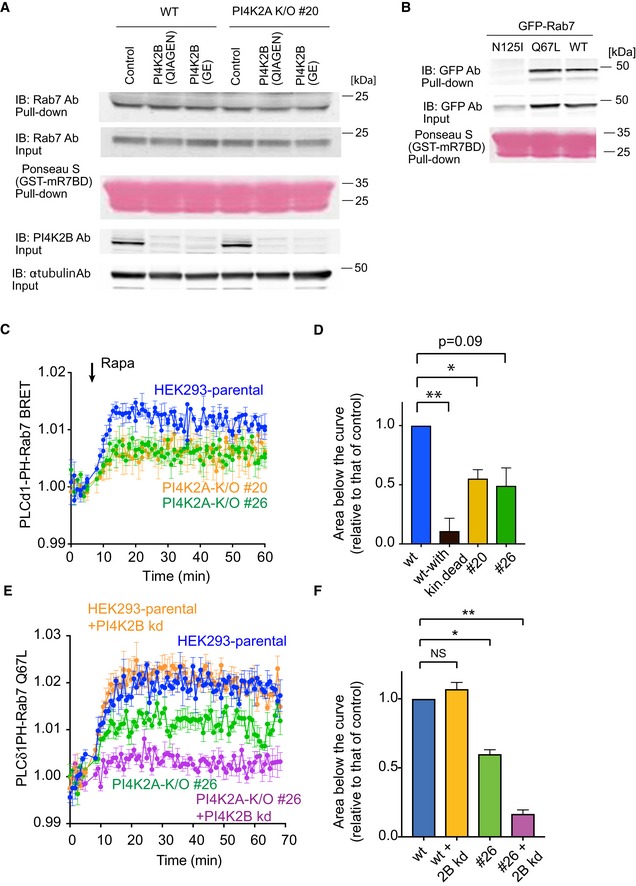
- Pull‐down assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods using lysates prepared from wild‐type or PI4K2A K/O cells #20 in which PI4K2B was knocked down by two different siRNAs (obtained from QIAGEN or GE). Whole‐cell lysates were collected 3 days after the transfection and active Rab7 captured by the Rab7‐GTP interacting motif of RILP. Western blot analysis of the captured material was performed with anti‐Rab7, anti‐PI4K2B, and anti‐alpha‐tubulin antibodies.
- Pull‐down assays showing the amount of overexpressed Rab7 wild‐type, N125I, Q67L mutant captured by the Rab7‐GTP binding domain.
- Increased production of PI(4,5)P2 in the Rab7 compartment by a recruited PIP5Kγ enzyme measured by BRET analysis in control and PI4K2A K/O cells. This panel originates from the same experiments shown in Fig 3C plotted separately for clarity (therefore, blue control curves are the same). For experimental details, see legend to Fig 3C. Means ± SEM from three separate experiments each performed in triplicates.
- This bar diagram shows the areas below the curves calculated from the time of rapamycin addition for each of four separate experiments similar to those shown in panel C (means ± SEM, n = 4). One‐way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons was used for statistical analysis (*P = 0.0204; **P = 0.0081).
- Knockdown (kd) of PI4K2B further reduces the amount of PI(4,5)P2 generated by a recruited PIP5Kγ in the Rab7 compartment. This experiment was performed similarly to that shown in Fig 3E using the Rab7‐QL mutant in the BRET construct. Means ± SEM from three separate experiments each performed in triplicates.
- Quantitation and statistical analysis of data shown in panel (E) performed as described for panel (D) (*P = 0.0118; **P = 0.0023).
Source data are available online for this figure.
