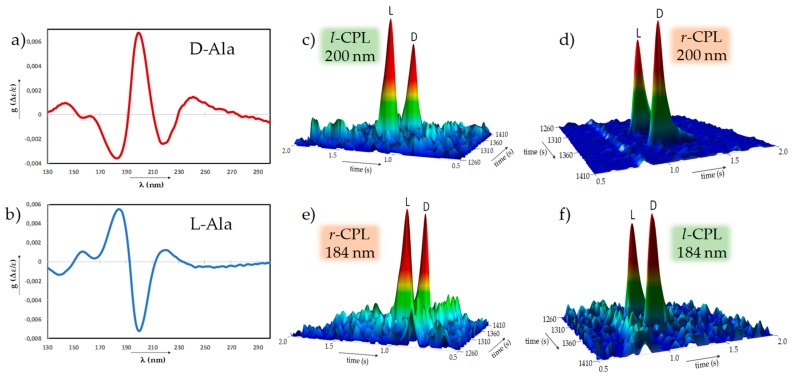
Figure 1.
Energy- and polarization-dependent CPL-induced enantiomeric excesses. (a, b) Anisotropy spectra in the vacuum UV and UV spectral range of enantiopure d-alanine (a) and l-alanine (b) in the solid state. (c–f) Close-up view of the multidimensional enantioselective gas chromatographic analysis of 13C-alanine enantiomers, after irradiation with CPL differing in helicity and energy. Amorphous racemic 13C-alanine was irradiated at 200 nm (6.19 eV), corresponding to the anisotropic maximum (a,b), with l-CPL resulting in a l-ee (c), and r-CPL resulting in the opposite ee value (d). Irradiation of amorphous racemic 13C-alanine at a wavelength of 184 nm (6.74 eV) with r- and l-CPL also induced opposite ees but they were flipped with regard to the wavelength of irradiation (e,f). CPL: circularly polarized light; UV: ultraviolet; ee: enantiomeric excess.