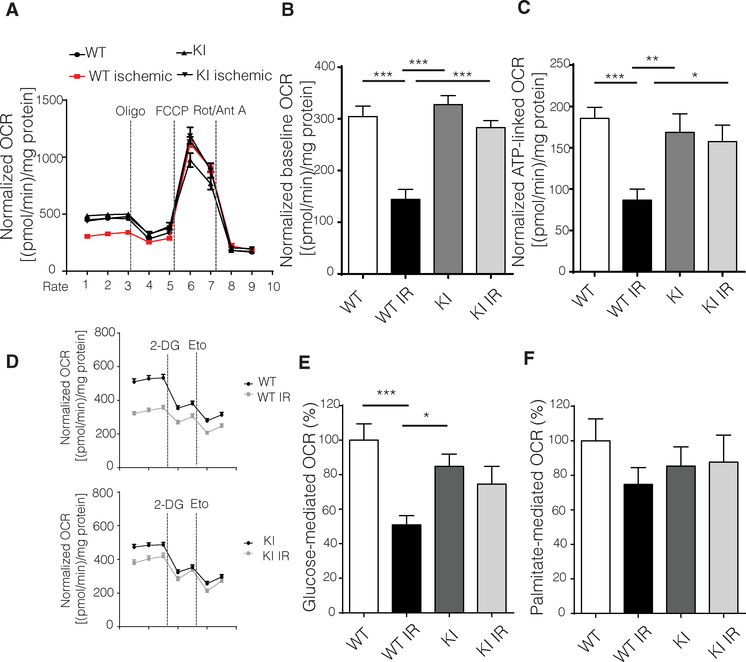
Fig. 3. Adult cardiomyocytes from GRK2-S670A KI mice post-IR injury maintain mitochondrial respiration and a normal glucose respiratory response.
(A) OCRs measured using a Seahorse flux analyzer in cardiomyocytes isolated from post-IR injury (24 hours) WT and KI mice (n = 44 to 47 wells per group; data from three hearts per genotype and all data normalized to total protein content). Oligo, oligomycin; Rot, rotenone; Ant A, antimycin A. (B) Quantification of basal respiration from data in (A); n same as in (A). (C) Quantification of ATP production from data in (A); n same as in (A). (D) Seahorse tracings of OCRs in cardiomyocytes from WT and KI mice post-IR injury normalized to protein content (n = 27 to 36 wells from three hearts per genotype). Eto, etomoxir. (E) Quantification of glucose- mediated respiration shown in (D); n values same as in (D). (F) Quantification of palmitate-mediated respiration shown in (D); n values same as in (D), ANOVA. Data are shown as means ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005.