Figure 3.
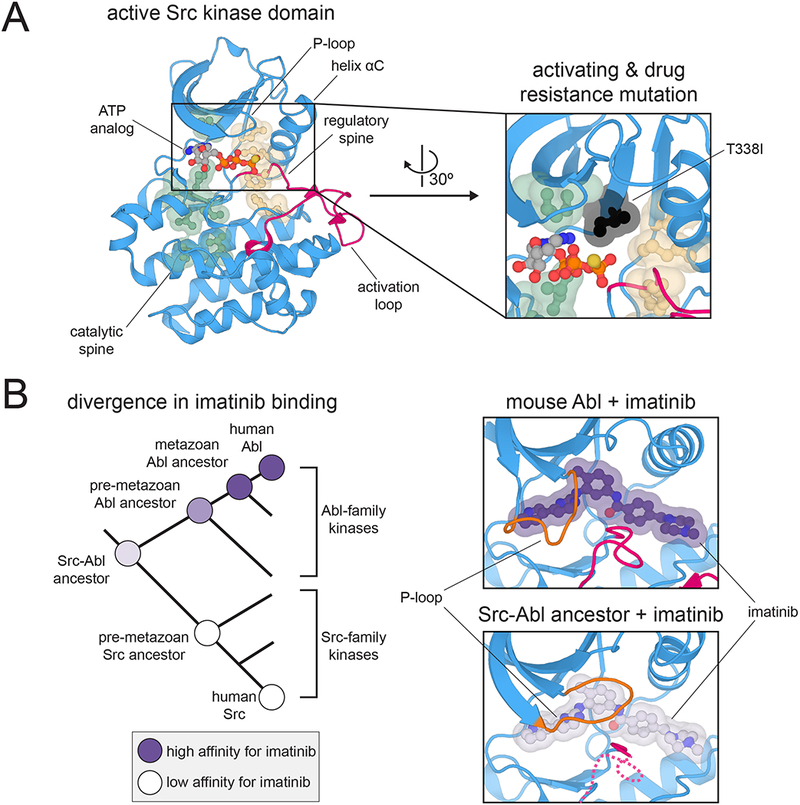
Sequence and structural features that control kinase dynamics and allostery. (A) Hydrophobic spines that control kinase activity and regulation. Left: Structure of the kinase domain of c-Src kinase in an active conformation, highlighting key structural elements and the hydrophobic spines (PDB code 3DQW). Right: Position of the T338I mutation (chicken c-Src numbering) relative to the hydrophobic spines. Mutations at this “gatekeeper” position in many kinases are often activating and confer resistance to ATP-competitive inhibitors (PDB code 3DQW). (B) Divergence of imatinib binding between the Src- and Abl-family kinases. Left: Phylogenetic tree depicting the divergence of Src- and Abl-family kinases, highlighting measured preferences at various nodes for binding to imatinib. Right: Closing of the P-loop over imatinib when bound to Abl but not a Src-Abl ancestral kinase (PDB codes 1OPJ and 4CSV).
