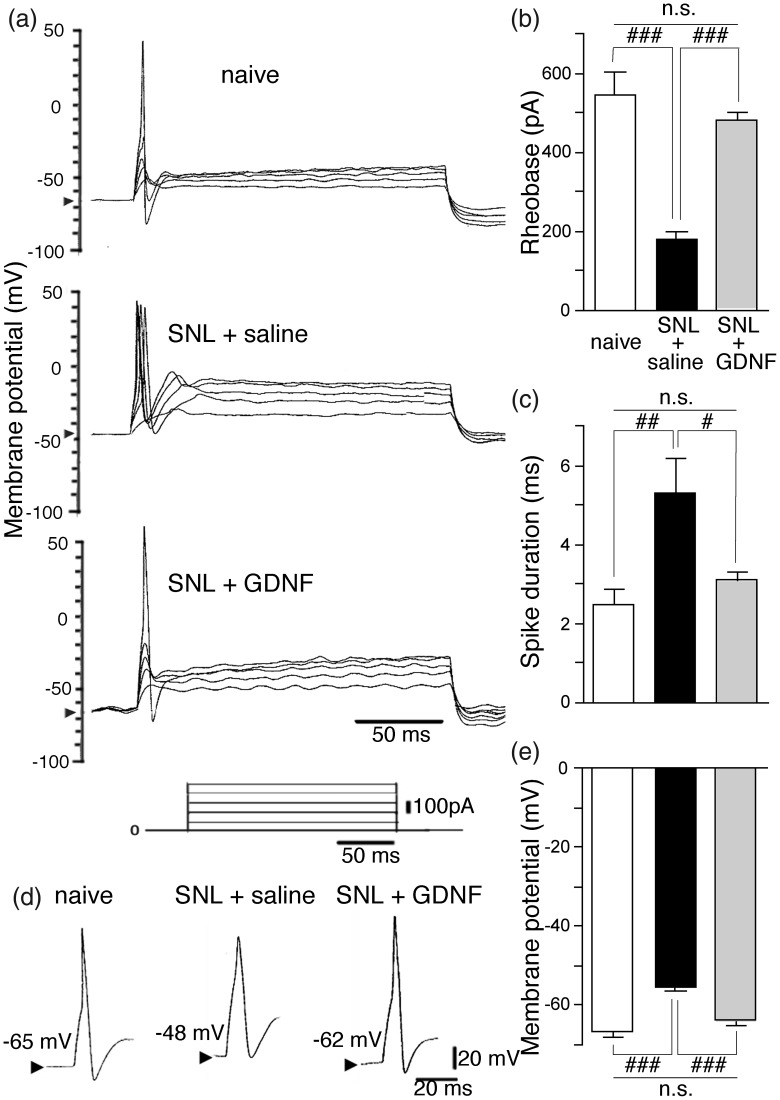
Figure 1.
Delayed GDNF treatment reversed SNL-induced hyperexcitability of injured large (diameter > 36 μm; exclusively with A-fiber) DRG neurons. (a) Changes in the excitability during depolarizing current pulses (200 ms, 100-pA step pulses) of the ipsilateral L5 DRG large neurons obtained from the indicated groups. Arrowheads in the y-axis indicate the resting membrane potentials. (b) Reversal of the rheobase (the minimum current required to elicit an action potential) in the injured large neurons by GDNF. (c) Reversal of spike duration in the injured large neurons by GDNF. (d) Representative shape of the first action potential in each group. Arrowheads indicate the resting membrane potentials. (e) Reversal of resting membrane potential in the injured large neurons by GDNF. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 7). n.s. P > 0.05, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests.
DRG: dorsal root ganglion; GDNF: glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; n.s.: not significant; SNL: spinal nerve ligation.