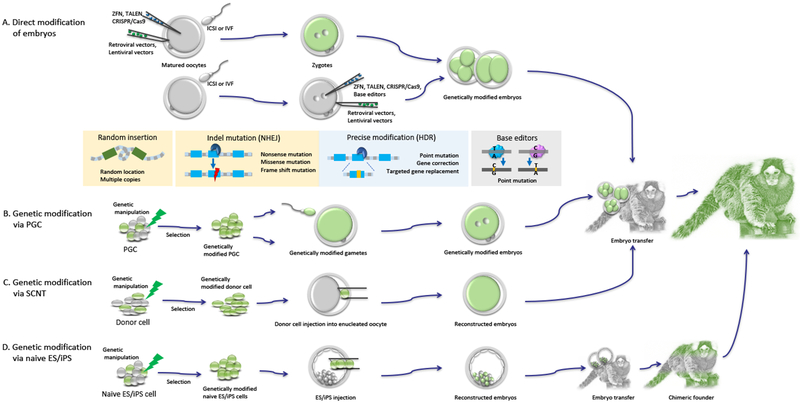
Figure 2:
Approaches to generate genetically modified NHP: (A) Injection of viral vectors into either oocytes or embryos results in random insertion and integration of multiple copies of the transgene into the genome with high efficiency, but it is not applicable for targeted gene modification. Programmable nucleases such as ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas9 are injected into fertilized oocytes to directly modify the embryo genome. (B-D) Precise targeted genetic manipulations of either PGC (B), somatic cells (C) or ES/iPS (D) are performed in cell cultures and the cells carrying the desired mutation are selected for production of genetically engineered NHP. See text for details. PGC: Primordial Germ Cells; SCNT: Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer; ES: Embryonic Stem cells; IPS: Induced Pluripotent Stem cells; ICSI: Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection; IVF: In Vitro Fertilization. ZFN: Zinc Finger Nuclease; TALEN: Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nuclease; CRISPR: Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats; Cas9:CRISPR ASsociated protein 9.