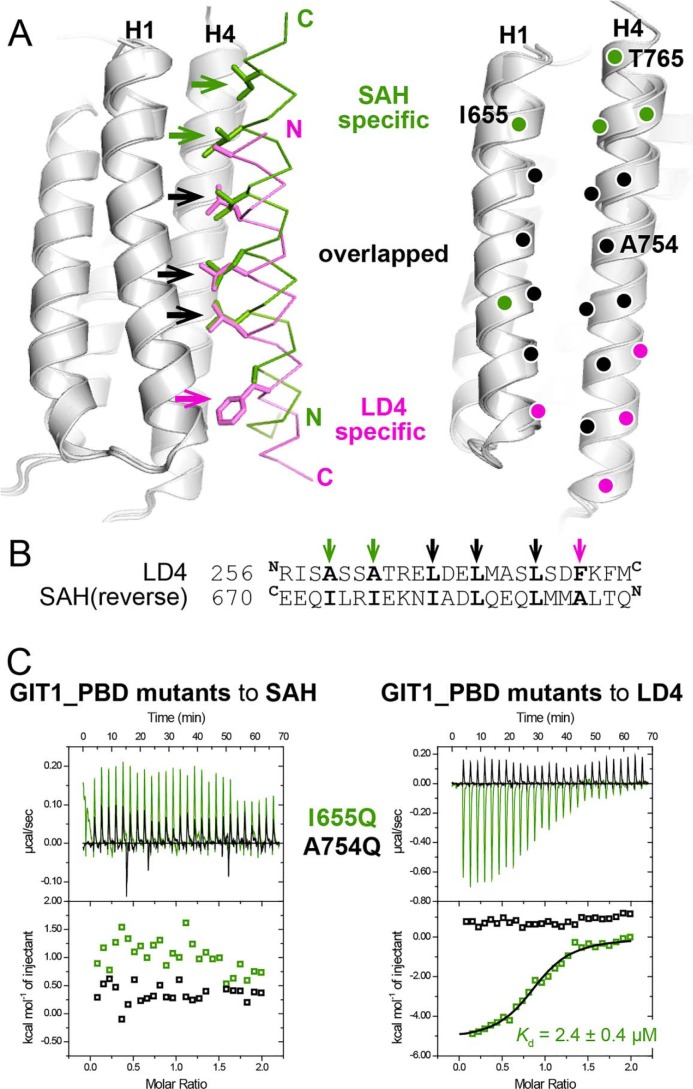
Figure 3.
The different binding modes of liprin-α2_SAH and paxillin-LD4 to GIT1_PBD. A, the superposition of the two complex structures revealing the different binding modes of GIT1_PBD. The hydrophobic residues of the LD4 and SAH peptide that are involved in the SAH-specific, LD4-specific, and overlapped interactions with the H1/H4 groove of GIT1_PBD are shown as a stick model and indicated by green, purple, and black arrows, respectively, in the left panel. The corresponding interacting residues of GIT1_PBD are indicated by purple, green, and black circles in the right panel. The residues that were analyzed by mutagenesis in this study are labeled with one-letter codes and position numbers. B, pairwise sequence alignment of the LD4 motif and the reversed sequence of the SAH peptide. C, ITC curves of the bindings of two GIT1_PBD mutants to liprin-α2_SAH and paxillin_LD4.