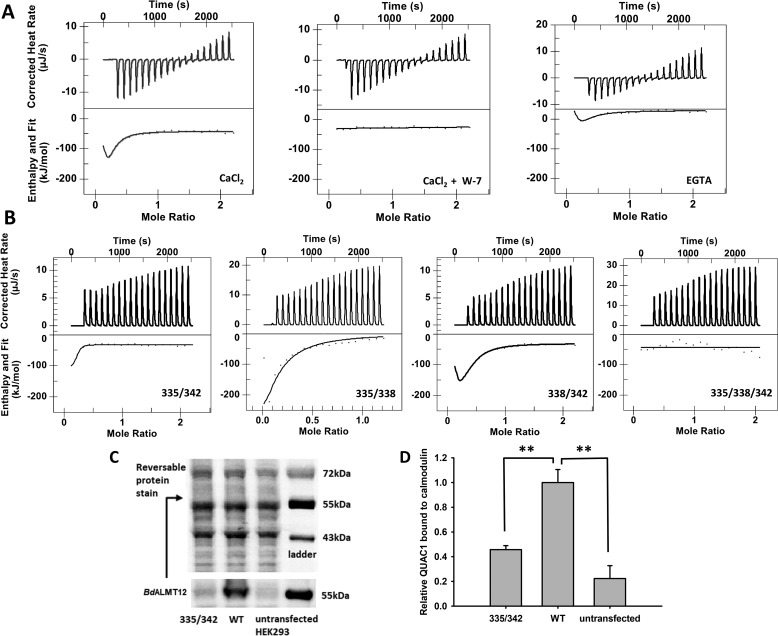
Figure 5.
Binding of WT and variant CaM-binding peptides to CaM. A, isothermal titration calorimetry analyses of the binding of WT to CaM in the presence of 5 mm Ca2+, 5 mm Ca2+ with 60 μm W-7, or no added Ca2+ with 1.5 mm EGTA for the 0 μm free Ca2+ effect. The amount of W-7 used in the above-mentioned experiment is equal to the amount of CaM presence (60 μm). The 5 mm Ca2+ and no Ca2+ data were fit using the “multiple sites” model, and the 5 mm Ca2+ with W-7 data were fit using the “independent” data. B, isothermal titration calorimetry analyses of the binding of variant CBD peptides to CaM. The binding of all peptides was carried out in the presence of 5 mm Ca2+. Variant 335/342 data were fit using the “multiple sites” model yielding a two-state binding result. The others were fit using the “independent” model and yielded either a single binding event (variant 335/338 and 335/342) or no binding (variant 335/338/342). C, representative Western blotting and reversible protein stain image of full-length WT QUAC1 and variant 335/342 binding to CaM. D, quantification of full-length QUAC1 protein bound to CaM. Wildtype BdALMT12 and variant 335/342 binding to CaM were analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-Myc tag antibody, n = 4. Wildtype and variant QUAC1 were quantified against total proteins eluted from the CaM affinity pulldown, and WT QUAC1 was normalized to 1. Error bars represent standard error. Significance was determined by one sample t test (** indicates p ≤ 0.01).