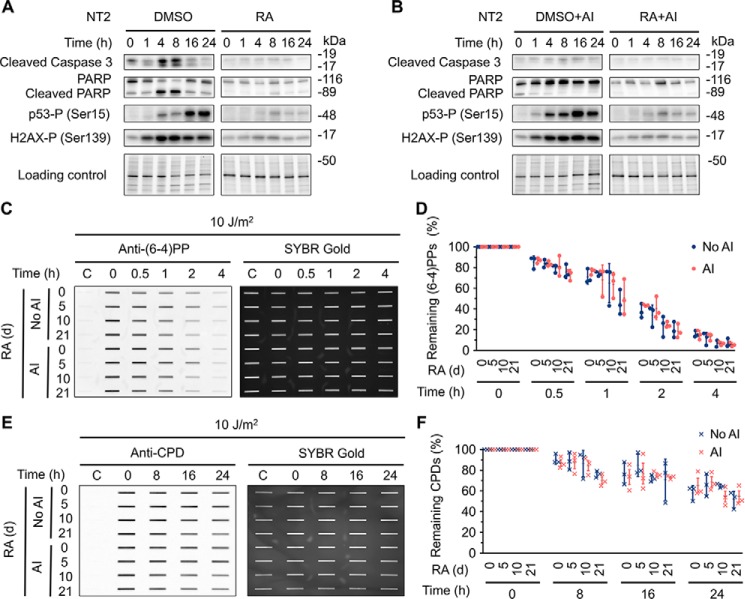
Figure 5.
Inhibition of apoptosis pathway has no effect on nucleotide excision repair capacity. A, NT2 cells were treated with 10 μm RA or 0.1% DMSO for 21 days. At the indicated time points following UV (10 J/m2) treatment, whole cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against the indicated proteins. Stain-free total protein staining was used as loading control. B, Western blotting assays were performed as in A except that apoptosis inhibitor (Z-VAD-FMK) was added 30 min prior to UV treatment. The final Z-VAD-FMK concentration was 20 μm. C and D, immunoslot blot assays showing repair rates of (6–4)PPs in NT2 cells at various differentiation stages after RA treatment. Repair rates of (6–4)PPs within 4 h after UV (10 J/m2) irradiation were analyzed as in Fig. 3, A–F except that apoptosis inhibitor (AI) was added 30 min prior to UV treatment. All experiments were repeated three times and representative results are shown. The results are presented as mean ± S.D. Statistical differences were tested by two-way ANOVA, followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons. No statistically significant difference was found. AI denotes group with apoptosis inhibitor treatment. No AI denotes control group. E and F, immunoslot blot assays showing repair rates of CPDs in NT2 cells at various differentiation stages after RA treatment. Repair rates within 24 h after UV (10 J/m2) irradiation were analyzed and presented as in C and D except that anti-CPD antibody was used. No statistically significant difference was found. AI denotes group with apoptosis inhibitor treatment. No AI denotes control group.